Preface ...................................................... xiii
On the Structure of Mathematics ............................... xix
Brief Summaries of Topics ................................... xxiii
0.1 Linear Algebra ...................................... xxiii
0.2 Real Analysis ....................................... xxiii
0.3 Differentiating Vector-Valued Functions ............. xxiii
0.4 Point Set Topology ................................... xxiv
0.5 Classical Stokes' Theorems ........................... xxiv
0.6 Differential Forms and Stokes' Theorem ............... xxiv
0.7 Curvature for Curves and Surfaces .................... xxiv
0.8 Geometry .............................................. xxv
0.9 Complex Analysis ...................................... xxv
0.10 Countability and the Axiom of Choice ................. xxvi
0.11 Algebra .............................................. xxvi
0.12 Lebesgue Integration ................................. xxvi
0.13 Fourier Analysis ..................................... xxvi
0.14 Differential Equations .............................. xxvii
0.15 Combinatorics and Probability Theory ................ xxvii
0.16 Algorithms .......................................... xxvii
1 Linear Algebra ............................................... 1
1.1 Introduction ............................................ 1
1.2 The Basic Vector Space 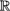 n ............................... 2
1.3 Vector Spaces and Linear Transformations ................ 4
1.4 Bases and Dimension ..................................... 6
1.5 The Determinant ......................................... 9
1.6 The Key Theorem of Linear Algebra ...................... 12
1.7 Similar Matrices ....................................... 14
1.8 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors ........................... 15
1.9 Dual Vector Spaces ..................................... 20
1.10 Books .................................................. 21
1.11 Exercises .............................................. 21
2 ε and δ Real Analysis ....................................... 23
2.1 Limits ................................................. 23
2.2 Continuity ............................................. 25
2.3 Differentiation ........................................ 26
2.4 Integration ............................................ 28
2.5 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus .................... 31
2.6 Pointwise Convergence of Functions ..................... 35
2.7 Uniform Convergence .................................... 36
2.8 The Weierstrass M-Test ................................. 38
2.9 Weierstrass' Example ................................... 40
2.10 Books .................................................. 43
2.11 Exercises .............................................. 44
3 Calculus for Vector-Valued Functions ........................ 47
3.1 Vector-Valued Functions ................................ 47
3.2 Limits and Continuity .................................. 49
3.3 Differentiation and Jacobians .......................... 50
3.4 The Inverse Function Theorem ........................... 53
3.5 Implicit Function Theorem .............................. 56
3.6 Books .................................................. 60
3.7 Exercises .............................................. 60
4 Point Set Topology .......................................... 63
4.1 Basic Definitions ...................................... 63
4.2 The Standard Topology on n ............................... 2
1.3 Vector Spaces and Linear Transformations ................ 4
1.4 Bases and Dimension ..................................... 6
1.5 The Determinant ......................................... 9
1.6 The Key Theorem of Linear Algebra ...................... 12
1.7 Similar Matrices ....................................... 14
1.8 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors ........................... 15
1.9 Dual Vector Spaces ..................................... 20
1.10 Books .................................................. 21
1.11 Exercises .............................................. 21
2 ε and δ Real Analysis ....................................... 23
2.1 Limits ................................................. 23
2.2 Continuity ............................................. 25
2.3 Differentiation ........................................ 26
2.4 Integration ............................................ 28
2.5 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus .................... 31
2.6 Pointwise Convergence of Functions ..................... 35
2.7 Uniform Convergence .................................... 36
2.8 The Weierstrass M-Test ................................. 38
2.9 Weierstrass' Example ................................... 40
2.10 Books .................................................. 43
2.11 Exercises .............................................. 44
3 Calculus for Vector-Valued Functions ........................ 47
3.1 Vector-Valued Functions ................................ 47
3.2 Limits and Continuity .................................. 49
3.3 Differentiation and Jacobians .......................... 50
3.4 The Inverse Function Theorem ........................... 53
3.5 Implicit Function Theorem .............................. 56
3.6 Books .................................................. 60
3.7 Exercises .............................................. 60
4 Point Set Topology .......................................... 63
4.1 Basic Definitions ...................................... 63
4.2 The Standard Topology on 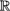 n ............................ 66
4.3 Metric Spaces .......................................... 72
4.4 Bases for Topologies ................................... 73
4.5 Zariski Topology of Commutative Rings .................. 75
4.6 Books .................................................. 77
4.7 Exercises .............................................. 78
5 Classical Stokes' Theorems .................................. 81
5.1 Preliminaries about Vector Calculus .................... 82
5.1.1 Vector Fields ................................... 82
5.1.2 Manifolds and Boundaries ........................ 84
5.1.3 Path Integrals .................................. 87
5.1.4 Surface Integrals ............................... 91
5.1.5 The Gradient .................................... 93
5.1.6 The Divergence .................................. 93
5.1.7 The Curl ........................................ 94
5.1.8 Orientability ................................... 94
5.2 The Divergence Theorem and Stokes' Theorem ............. 95
5.3 Physical Interpretation of Divergence Thm .............. 97
5.4 A Physical Interpretation of Stokes' Theorem ........... 98
5.5 Proof of the Divergence Theorem ........................ 99
5.6 Sketch of a Proof for Stokes' Theorem ................. 104
5.7 Books ................................................. 108
5.8 Exercises ............................................. 108
6 Differential Forms and Stokes' Thm. ........................ 111
6.1 Volumes of Parallelepipeds ............................ 112
6.2 Diff. Forms and the Exterior Derivative ............... 115
6.2.1 Elementary k-forms ............................. 115
6.2.2 The Vector Space of k-forms .................... 118
6.2.3 Rules for Manipulating k-forms ................. 119
6.2.4 Differential k-forms and the Exterior
Derivative ..................................... 122
6.3 Differential Forms and Vector Fields .................. 124
6.4 Manifolds ............................................. 126
6.5 Tangent Spaces and Orientations ....................... 132
6.5.1 Tangent Spaces for Implicit and Parametric
Manifolds ...................................... 132
6.5.2 Tangent Spaces for Abstract Manifolds .......... 133
6.5.3 Orientation of a Vector Space .................. 135
6.5.4 Orientation of a Manifold and its Boundary ..... 136
6.6 Integration on Manifolds .............................. 137
6.7 Stokes' Theorem ....................................... 139
6.8 Books ................................................. 142
6.9 Exercises ............................................. 143
7 Curvature for Curves and Surfaces .......................... 145
7.1 Plane Curves .......................................... 145
7.2 Space Curves .......................................... 148
7.3 Surfaces .............................................. 152
7.4 The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem .............................. 157
7.5 Books ................................................. 158
7.6 Exercises ............................................. 158
8 Geometry ................................................... 161
8.1 Euclidean Geometry .................................... 162
8.2 Hyperbolic Geometry ................................... 163
8.3 Elliptic Geometry ..................................... 166
8.4 Curvature ............................................. 167
8.5 Books ................................................. 168
8.6 Exercises ............................................. 169
9 Complex Analysis ........................................... 171
9.1 Analyticity as a Limit ................................ 172
9.2 Cauchy-Riemann Equations .............................. 174
9.3 Integral Representations of Functions ................. 179
9.4 Analytic Functions as Power Series .................... 187
9.5 Conformal Maps ........................................ 191
9.6 The Riemann Mapping Theorem ........................... 194
9.7 Several Complex Variables: Hartog's Theorem ........... 196
9.8 Books ................................................. 197
9.9 Exercises ............................................. 198
10 Countability and the Axiom of Choice ....................... 201
10.1 Countability .......................................... 201
10.2 Naive Set Theory and Paradoxes ........................ 205
10.3 The Axiom of Choice ................................... 207
10.4 Non-measurable Sets ................................... 208
10.5 Gödel and Independence Proofs ......................... 210
10.6 Books ................................................. 211
10.7 Exercises ............................................. 211
11 Algebra .................................................... 213
11.1 Groups ................................................ 213
11.2 Representation Theory ................................. 219
11.3 Rings ................................................. 221
11.4 Fields and Galois Theory .............................. 223
11.5 Books ................................................. 228
11.6 Exercises ............................................. 229
12 Lebesgue Integration ....................................... 231
12.1 Lebesgue Measure ...................................... 231
12.2 The Cantor Set ........................................ 234
12.3 Lebesgue Integration .................................. 236
12.4 Convergence Theorems .................................. 239
12.5 Books ................................................. 241
12.6 Exercises ............................................. 241
13 Fourier Analysis ........................................... 243
13.1 Waves, Periodic Functions and Trigonometry ............ 243
13.2 Fourier Series ........................................ 244
13.3 Convergence Issues .................................... 250
13.4 Fourier Integrals ала Transforms ...................... 252
13.5 Solving Differential Equations ........................ 256
13.6 Books ................................................. 258
13.7 Exercises ............................................. 258
14 Differential Equations ..................................... 261
14.1 Basics ................................................ 261
14.2 Ordinary Differential Equations ....................... 262
14.3 The Laplacian ......................................... 266
14.3.1 Mean Value Principle .......................... 266
14.3.2 Separation of Variables ....................... 267
14.3.3 Applications to Complex Analysis .............. 270
14.4 The Heat Equation ..................................... 270
14.5 The Wave Equation ..................................... 273
14.5.1 Derivation ..................................... 273
14.5.2 Change of Variables ............................ 277
14.6 Integrability Conditions .............................. 279
14.7 Lewy's Example ........................................ 281
14.8 Books ................................................. 282
14.9 Exercises ............................................. 282
15 Combinatorics and Probability .............................. 285
15.1 Counting .............................................. 285
15.2 Basic Probability Theory .............................. 287
15.3 Independence .......................................... 290
15.4 Expected Values and Variance .......................... 291
15.5 Central Limit Theorem ................................. 294
15.6 Stirling's Approximation for n ........................ 300
15.7 Books ................................................. 305
15.8 Exercises ............................................. 305
16 Algorithms ................................................. 307
16.1 Algorithms and Complexity ............................. 308
16.2 Graphs: Euler and Hamiltonian Circuits ................ 308
16.3 Sorting and Trees ..................................... 313
16.4 P=NP? ................................................. 316
16.5 Numerical Analysis: Newton's Method ................... 317
16.6 Books ................................................. 324
16.7 Exercises ............................................. 324
A Equivalence Relations ...................................... 327 n ............................ 66
4.3 Metric Spaces .......................................... 72
4.4 Bases for Topologies ................................... 73
4.5 Zariski Topology of Commutative Rings .................. 75
4.6 Books .................................................. 77
4.7 Exercises .............................................. 78
5 Classical Stokes' Theorems .................................. 81
5.1 Preliminaries about Vector Calculus .................... 82
5.1.1 Vector Fields ................................... 82
5.1.2 Manifolds and Boundaries ........................ 84
5.1.3 Path Integrals .................................. 87
5.1.4 Surface Integrals ............................... 91
5.1.5 The Gradient .................................... 93
5.1.6 The Divergence .................................. 93
5.1.7 The Curl ........................................ 94
5.1.8 Orientability ................................... 94
5.2 The Divergence Theorem and Stokes' Theorem ............. 95
5.3 Physical Interpretation of Divergence Thm .............. 97
5.4 A Physical Interpretation of Stokes' Theorem ........... 98
5.5 Proof of the Divergence Theorem ........................ 99
5.6 Sketch of a Proof for Stokes' Theorem ................. 104
5.7 Books ................................................. 108
5.8 Exercises ............................................. 108
6 Differential Forms and Stokes' Thm. ........................ 111
6.1 Volumes of Parallelepipeds ............................ 112
6.2 Diff. Forms and the Exterior Derivative ............... 115
6.2.1 Elementary k-forms ............................. 115
6.2.2 The Vector Space of k-forms .................... 118
6.2.3 Rules for Manipulating k-forms ................. 119
6.2.4 Differential k-forms and the Exterior
Derivative ..................................... 122
6.3 Differential Forms and Vector Fields .................. 124
6.4 Manifolds ............................................. 126
6.5 Tangent Spaces and Orientations ....................... 132
6.5.1 Tangent Spaces for Implicit and Parametric
Manifolds ...................................... 132
6.5.2 Tangent Spaces for Abstract Manifolds .......... 133
6.5.3 Orientation of a Vector Space .................. 135
6.5.4 Orientation of a Manifold and its Boundary ..... 136
6.6 Integration on Manifolds .............................. 137
6.7 Stokes' Theorem ....................................... 139
6.8 Books ................................................. 142
6.9 Exercises ............................................. 143
7 Curvature for Curves and Surfaces .......................... 145
7.1 Plane Curves .......................................... 145
7.2 Space Curves .......................................... 148
7.3 Surfaces .............................................. 152
7.4 The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem .............................. 157
7.5 Books ................................................. 158
7.6 Exercises ............................................. 158
8 Geometry ................................................... 161
8.1 Euclidean Geometry .................................... 162
8.2 Hyperbolic Geometry ................................... 163
8.3 Elliptic Geometry ..................................... 166
8.4 Curvature ............................................. 167
8.5 Books ................................................. 168
8.6 Exercises ............................................. 169
9 Complex Analysis ........................................... 171
9.1 Analyticity as a Limit ................................ 172
9.2 Cauchy-Riemann Equations .............................. 174
9.3 Integral Representations of Functions ................. 179
9.4 Analytic Functions as Power Series .................... 187
9.5 Conformal Maps ........................................ 191
9.6 The Riemann Mapping Theorem ........................... 194
9.7 Several Complex Variables: Hartog's Theorem ........... 196
9.8 Books ................................................. 197
9.9 Exercises ............................................. 198
10 Countability and the Axiom of Choice ....................... 201
10.1 Countability .......................................... 201
10.2 Naive Set Theory and Paradoxes ........................ 205
10.3 The Axiom of Choice ................................... 207
10.4 Non-measurable Sets ................................... 208
10.5 Gödel and Independence Proofs ......................... 210
10.6 Books ................................................. 211
10.7 Exercises ............................................. 211
11 Algebra .................................................... 213
11.1 Groups ................................................ 213
11.2 Representation Theory ................................. 219
11.3 Rings ................................................. 221
11.4 Fields and Galois Theory .............................. 223
11.5 Books ................................................. 228
11.6 Exercises ............................................. 229
12 Lebesgue Integration ....................................... 231
12.1 Lebesgue Measure ...................................... 231
12.2 The Cantor Set ........................................ 234
12.3 Lebesgue Integration .................................. 236
12.4 Convergence Theorems .................................. 239
12.5 Books ................................................. 241
12.6 Exercises ............................................. 241
13 Fourier Analysis ........................................... 243
13.1 Waves, Periodic Functions and Trigonometry ............ 243
13.2 Fourier Series ........................................ 244
13.3 Convergence Issues .................................... 250
13.4 Fourier Integrals ала Transforms ...................... 252
13.5 Solving Differential Equations ........................ 256
13.6 Books ................................................. 258
13.7 Exercises ............................................. 258
14 Differential Equations ..................................... 261
14.1 Basics ................................................ 261
14.2 Ordinary Differential Equations ....................... 262
14.3 The Laplacian ......................................... 266
14.3.1 Mean Value Principle .......................... 266
14.3.2 Separation of Variables ....................... 267
14.3.3 Applications to Complex Analysis .............. 270
14.4 The Heat Equation ..................................... 270
14.5 The Wave Equation ..................................... 273
14.5.1 Derivation ..................................... 273
14.5.2 Change of Variables ............................ 277
14.6 Integrability Conditions .............................. 279
14.7 Lewy's Example ........................................ 281
14.8 Books ................................................. 282
14.9 Exercises ............................................. 282
15 Combinatorics and Probability .............................. 285
15.1 Counting .............................................. 285
15.2 Basic Probability Theory .............................. 287
15.3 Independence .......................................... 290
15.4 Expected Values and Variance .......................... 291
15.5 Central Limit Theorem ................................. 294
15.6 Stirling's Approximation for n ........................ 300
15.7 Books ................................................. 305
15.8 Exercises ............................................. 305
16 Algorithms ................................................. 307
16.1 Algorithms and Complexity ............................. 308
16.2 Graphs: Euler and Hamiltonian Circuits ................ 308
16.3 Sorting and Trees ..................................... 313
16.4 P=NP? ................................................. 316
16.5 Numerical Analysis: Newton's Method ................... 317
16.6 Books ................................................. 324
16.7 Exercises ............................................. 324
A Equivalence Relations ...................................... 327
|