Preface to the Second Edition .................................. ix
Introduction .................................................... 1
Notation ....................................................... 18
I Gradient Flow in Metric Spaces .............................. 21
1 Curves and Gradients in Metric Spaces ....................... 23
1.1 Absolutely continuous curves and metric derivative ..... 23
1.2 Upper gradients ........................................ 26
1.3 Curves of maximal slope ................................ 30
1.4 Curves of maximal slope in Hilbert and Banach spaces ... 32
2 Existence of Curves of Maximal Slope ........................ 39
2.1 Main topological assumptions ........................... 42
2.2 Solvability of the discrete problem and compactness
of discrete trajectories ............................... 44
2.3 Generalized minimizing movements and curves of
maximal slope .......................................... 45
2.4 The (geodesically) convex case ......................... 49
3 Proofs of the Convergence Theorems .......................... 59
3.1 Moreau-Yosida approximation ............................ 59
3.2 A priori estimates for the discrete solutions .......... 66
3.3 A compactness argument ................................. 69
3.4 Conclusion of the proofs of the convergence theorems ... 71
4 Generation of Contraction Semigroups ........................ 75
4.1 Cauchy-type estimates for discrete solutions ........... 82
4.1.1 Discrete variational inequalities ............... 82
4.1.2 Piecewise affine interpolation and comparison
results ......................................... 84
4.2 Convergence of discrete solutions ...................... 89
4.2.1 Convergence when the initial datum u0 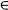 D(Ø) .... 89
4.2.2 Convergence when the initial datum u0 D(Ø) .... 89
4.2.2 Convergence when the initial datum u0 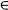 D(Ø) .... 92
4.3 Regularizing effect, uniqueness and the semigroup
property ............................................... 93
4.4 Optimal error estimates ................................ 97
4.4.1 The case λ = 0 .................................. 97
4.4.2 The case λ ≠ 0 .................................. 99
II Gradient Flow in the Space of Probability Measures ........ 103
5 Preliminary Results on Measure Theory ...................... 105
5.1 Narrow convergence, tightness, and uniform
integrability ......................................... 106
5.1.1 Unbounded and l.s.c. integrands ................ 109
5.1.2 Hilbert spaces and weak topologies ............. 113
5.2 Transport of measures ................................. 118
5.3 Measure-valued maps and disintegration theorem ........ 121
5.4 Convergence of plans and convergence of maps .......... 124
5.5 Approximate differentiability and area formula in
Euclidean spaces ...................................... 128
6 The Optimal Transportation Problem ......................... 133
6.1 Optimality conditions ................................. 135
6.2 Optimal transport maps and their regularity ........... 139
6.2.1 Approximate differentiability of the optimal
transport map .................................. 142
6.2.2 The infinite dimensional case .................. 147
6.2.3 The quadratic case p = 2 ....................... 149
7 The Wasserstein Distance and its Behaviour along
Geodesies .................................................. 151
7.1 The Wasserstein distance .............................. 151
7.2 Interpolation and geodesies ........................... 158
7.3 The curvature properties of D(Ø) .... 92
4.3 Regularizing effect, uniqueness and the semigroup
property ............................................... 93
4.4 Optimal error estimates ................................ 97
4.4.1 The case λ = 0 .................................. 97
4.4.2 The case λ ≠ 0 .................................. 99
II Gradient Flow in the Space of Probability Measures ........ 103
5 Preliminary Results on Measure Theory ...................... 105
5.1 Narrow convergence, tightness, and uniform
integrability ......................................... 106
5.1.1 Unbounded and l.s.c. integrands ................ 109
5.1.2 Hilbert spaces and weak topologies ............. 113
5.2 Transport of measures ................................. 118
5.3 Measure-valued maps and disintegration theorem ........ 121
5.4 Convergence of plans and convergence of maps .......... 124
5.5 Approximate differentiability and area formula in
Euclidean spaces ...................................... 128
6 The Optimal Transportation Problem ......................... 133
6.1 Optimality conditions ................................. 135
6.2 Optimal transport maps and their regularity ........... 139
6.2.1 Approximate differentiability of the optimal
transport map .................................. 142
6.2.2 The infinite dimensional case .................. 147
6.2.3 The quadratic case p = 2 ....................... 149
7 The Wasserstein Distance and its Behaviour along
Geodesies .................................................. 151
7.1 The Wasserstein distance .............................. 151
7.2 Interpolation and geodesies ........................... 158
7.3 The curvature properties of 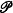 2(X) ..................... 160
8 A.C. Curves in 2(X) ..................... 160
8 A.C. Curves in 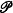 p(X) and the Continuity Equation ........... 167
8.1 The continuity equation in p(X) and the Continuity Equation ........... 167
8.1 The continuity equation in  d ......................... 169
8.2 A probabilistic representation of solutions of the
continuity equation ................................... 178
8.3 Absolutely continuous curves in d ......................... 169
8.2 A probabilistic representation of solutions of the
continuity equation ................................... 178
8.3 Absolutely continuous curves in  p(X) ................. 182
8.4 The tangent bundle to p(X) ................. 182
8.4 The tangent bundle to  p(X) ........................... 189
8.5 Tangent space and optimal maps ........................ 194
9 Convex Functionals in p(X) ........................... 189
8.5 Tangent space and optimal maps ........................ 194
9 Convex Functionals in  p(X) ................................ 201
9.1 A-geodesically convex functionals in p(X) ................................ 201
9.1 A-geodesically convex functionals in 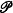 p(X) ............ 202
9.2 Convexity along generalized geodesies ................. 205
9.3 Examples of convex functionals in p(X) ............ 202
9.2 Convexity along generalized geodesies ................. 205
9.3 Examples of convex functionals in 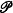 p(X) ............... 209
9.4 Relative entropy and convex functionals of
measures .............................................. 215
9.4.1 Log-concavity and displacement convexity ....... 220
10 Metric Slope and Subdifferential Calculus in p(X) ............... 209
9.4 Relative entropy and convex functionals of
measures .............................................. 215
9.4.1 Log-concavity and displacement convexity ....... 220
10 Metric Slope and Subdifferential Calculus in 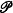 p(X) ......... 227
10.1 Subdifferential calculus in p(X) ......... 227
10.1 Subdifferential calculus in 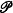 r2(X): the regular
case ........................................... 229
10.1.1 The case of A-convex functionals along
geodesies ...................................... 231
10.1.2 Regular functionals ............................ 232
10.2 Differentiability properties of the p-Wasserstein
distance .............................................. 234
10.3 Subdifferential calculus in r2(X): the regular
case ........................................... 229
10.1.1 The case of A-convex functionals along
geodesies ...................................... 231
10.1.2 Regular functionals ............................ 232
10.2 Differentiability properties of the p-Wasserstein
distance .............................................. 234
10.3 Subdifferential calculus in 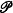 p(X): the general
case .................................................. 240
10.3.1 The case of λ-convex functionals along
geodesies ...................................... 244
10.3.2 Regular functionals ............................ 246
10.4 Example of subdifferentials ........................... 254
10.4.1 Variational integrals: the smooth case ......... 254
10.4.2 The potential energy ........................... 255
10.4.3 The internal energy ............................ 257
10.4.4 The relative internal energy ................... 265
10.4.5 The interaction energy ......................... 267
10.4.6 The opposite Wasserstein distance .............. 269
10.4.7 The sum of internal, potential and
interaction energy ............................. 272
10.4.8 Relative entropy and Fisher information in
infinite dimensions ............................ 276
11 Gradient Flows and Curves of Maximal Slope in p(X): the general
case .................................................. 240
10.3.1 The case of λ-convex functionals along
geodesies ...................................... 244
10.3.2 Regular functionals ............................ 246
10.4 Example of subdifferentials ........................... 254
10.4.1 Variational integrals: the smooth case ......... 254
10.4.2 The potential energy ........................... 255
10.4.3 The internal energy ............................ 257
10.4.4 The relative internal energy ................... 265
10.4.5 The interaction energy ......................... 267
10.4.6 The opposite Wasserstein distance .............. 269
10.4.7 The sum of internal, potential and
interaction energy ............................. 272
10.4.8 Relative entropy and Fisher information in
infinite dimensions ............................ 276
11 Gradient Flows and Curves of Maximal Slope in 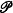 p(X) ........ 279
11.1 The gradient flow equation and its metric
formulations .......................................... 280
11.1.1 Gradient flows and curves of maximal slope ..... 283
11.1.2 Gradient flows for λ-convex functionals ........ 284
11.1.3 The convergence of the "Minimizing Movement"
scheme ......................................... 286
11.2 Gradient flows for λ-convex functionals along
generalized geodesies ................................. 295
11.2.1 Applications to Evolution PDE's ................ 298
11.3 Gradient flows in p(X) ........ 279
11.1 The gradient flow equation and its metric
formulations .......................................... 280
11.1.1 Gradient flows and curves of maximal slope ..... 283
11.1.2 Gradient flows for λ-convex functionals ........ 284
11.1.3 The convergence of the "Minimizing Movement"
scheme ......................................... 286
11.2 Gradient flows for λ-convex functionals along
generalized geodesies ................................. 295
11.2.1 Applications to Evolution PDE's ................ 298
11.3 Gradient flows in 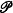 p(X) for regular functionals ....... 304
12 Appendix ................................................... 307
12.1 Caratheodory and normal integrands .................... 307
12.2 Weak convergence of plans and disintegrations ......... 308
12.3 PC metric spaces and their geometric tangent cone ..... 310
12.4 The geometric tangent spaces in p(X) for regular functionals ....... 304
12 Appendix ................................................... 307
12.1 Caratheodory and normal integrands .................... 307
12.2 Weak convergence of plans and disintegrations ......... 308
12.3 PC metric spaces and their geometric tangent cone ..... 310
12.4 The geometric tangent spaces in 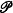 2(X) ................. 314
Bibliography .................................................. 331
Index ......................................................... 333 2(X) ................. 314
Bibliography .................................................. 331
Index ......................................................... 333
|