1 MATRIX ALGEBRA
1.1 Notations, Definitions, and Identities .................. 1
1.2 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors ............................ 7
1.3 Diagonalization of Simple and Semisimple Matrices ...... 10
1.4 Nonsemisimpie Matrices ................................. 11
1.5 Commutative Matrices ................................... 16
1.6 Positive Definite Real Matrices ........................ 18
1.7 Hermitian Matrices ..................................... 21
1.8 Eigenplane ............................................. 25
1.9 Square Roots of a Matrix ............................... 27
2 LINEAR ANISOTROPIC ELASTIC MATERIALS
2.1 Elastic Stiffnesses .................................... 32
2.2 Elastic Compliances .................................... 34
2.3 Contracted Notations ................................... 35
2.4 Reduced Elastic Compliances ............................ 37
2.5 Material Symmetry ...................................... 40
2.6 Matrix С for Materials with Symmetry Planes ............ 43
2.7 Matrices s and s' for Materials with Symmetry Planes ... 51
2.8 Transformation of С and s .............................. 53
2.9 Restrictions on Elastic Constants ...................... 56
2.10 Determination of Symmetry Planes ....................... 59
3 ANTIPLANE DEFORMATIONS
3.1 Uncoupling of Inplane and Antiplane Displacements ...... 65
3.2 Plane Stress Deformations .............................. 67
3.3 General Solutions for Antiplane Deformations ........... 69
3.4 The Complex Functions lnz and √z2 - α2 ................. 72
3.5 Green's Functions for Infinite Space and Half-Space .... 75
3.6 Green's Function for Bimaterials ....................... 80
3.7 Mapping of an Ellipse to a Circle for z=xl+px2 .......... 83
3.8 Infinite Space with an Elliptic Hole or an Elliptic
Rigid Inclusion ........................................ 90
3.9 Anisotropic Elliptic Body .............................. 95
3.10 Green's Functions for an Elliptic Inclusion ........... 100
3.11 A Crack in an Infinite Space and Bimaterials .......... 109
3.12 Infinite Space with a Hole of Arbitrary Shape ......... 114
3.13 Remarks ............................................... 116
3.14 A Theorem ............................................. 117
4 THE LEKHNITSKII FORMALISM
4.1 The Airy Function χ and the Stress Function Ψ ......... 118
4.2 Displacements for Two-Dimensional Stresses ............ 119
4.3 Differential Equations for χ an Ψ ..................... 121
4.4 Eigenvalues p ......................................... 123
4.5 Anisotropic Materials with p1=p2=p3 .................... 125
4.6 Representation of General Solutions ................... 128
4.7 Dependence of Solutions on Elastic Constants .......... 131
5 THE STROH FORMALISM
5.1 The Eshelby-Reid-Shockley Formalism ................... 134
5.2 Eigenvalues p ......................................... 136
5.3 The Sextic Formalism of Stroh ......................... 139
5.4 The Stress Function 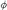 and the Airy Function χ ......... 142
5.5 Orthogonality and Closure Relations ................... 144
5.6 Positive Definite Hermitian Matrices .................. 147
5.7 The Matrix Differential Equation ...................... 149
5.8 Physical Meanings of p, α, and b ...................... 152
5.9 Nonsemisimple N ....................................... 153
5.10 Dependence of Solutions on Elastic Constants ......... 156
5.11 A.N. Stroh (1926-1962) ............................... 159
6 THE STRUCTURES AND IDENTITIES OF THE ELASTICITY MATRICES
6.1 The Structure of Nj ................................... 164
6.2 The Structure of Nj(-1) ................................ 168
6.3 Explicit Expressions of A and B ....................... 170
6.4 Explicit Expressions of S, H, and L ................... 172
6.5 Identities Relating S, H, and L ....................... 175
6.6 The Structure of S, H, and L .......................... 179
6.7 Classification of the Eigenvectors ej and ej .......... 186
6.8 Commutative 6x6 Matrices .............................. 194
6.9 Identities Connecting p, A, and В to Real Matrices .... 196
6.10 Eigenvectors of the Extraordinary Semisimple Matrix
N ..................................................... 199
7 TRANSFORMATION OF THE ELASTICITY MATRICES AND DUAL
COORDINATE SYSTEMS
7.1 Eigenvalues p(θ) ...................................... 201
7.2 Elasticity Matrices in a Rotated Coordinate System .... 207
7.3 Sextic Formalism in Dual Coordinate Systems ........... 210
7.4 Nonsemisimple N(θ) .................................... 215
7.5 Properties of N(θ) and Nj(θ) .......................... 218
7.6 The Barnett-Lothe Integral Formalism .................. 222
7.7 Invariants of S, H, and L ............................. 224
7.8 Commutative 6x6 Matrices .............................. 228
7.9 Identities Connecting A, B, and ƒ(z) to Real
Matrices .............................................. 230
7.10 General Solutions and Identities in Dual Coordinate
Systems ............................................... 235
7.11 The Tensors G1(θ) and G3(θ) ........................... 240
8 GREENS FUNCTIONS FOR INFINITE SPACE, HALF-SPACE, AND
COMPOSITE SPACE
8.1 Line Force and Line Dislocation in Infinite Space ..... 243
8.2 One-Component Green's Functions ....................... 250
8.3 Physical Meanings of the Eigenvectors ej and ej ....... 252
8.4 Interaction of Two Line Dislocations .................. 255
8.5 Surface Green's Function .............................. 258
8.6 Green's Functions for Half-Space ...................... 260
8.7 Image Singularities ................................... 268
8.8 Interfacial Green's Function .......................... 273
8.9 Green's Function for Bimaterials ...................... 283
8.10 Composite Space and Composite Wedge ................... 291
8.11 Angularly Inhomogeneous Space and Wedge ............... 295
8.12 Green's Functions for Concentrated Couple, Double
Force, and Other Higher Order Singularities ........... 298
8.13 Wedge Under a Concentrated Couple ..................... 311
9 PARTICULAR SOLUTIONS, STRESS SINGULARITIES, AND STRESS
DECAY
9.1 Wedge Subjected to Tractions .......................... 316
9.2 Nonuniform Stress Solutions in a Wedge ................ 320
9.3 Solutions for Critical Wedge Angles ................... 325
9.4 Eigenfunctions for a Wedge ............................ 329
9.5 Stress Singularities for Wedge Angles к and In ........ 337
9.6 Stress Singularities at an Interfacial Crack .......... 341
9.7 Singularities of the Form rδ(lnr)n .................... 348
9.8 Singularities Due to Curved Boundaries ................ 352
9.9 Existence of a Singularity ............................ 356
9.10 Stress Decay in an Anisotropic Elastic Strip .......... 357
10 ANISOTROPIC MATERIALS WITH AN ELLIPTIC BOUNDARY
10.1 A Force Applied to an Elliptic Rigid Inclusion ........ 365
10.2 A Moment Applied to an Elliptic Rigid Inclusion ....... 369
10.3 Green's Functions for Elliptic Hole or Rigid
Inclusion ............................................. 371
10.4 Surface Green's Function for an Elliptic Hole ......... 376
10.5 Representations of a Uniform Stress Solution .......... 378
10.6 Elliptic Hole or Rigid Inclusion Subjected to
a Uniform Loading at Infinity ......................... 380
10.7 Elliptic Elastic Inclusion Subjected to a Uniform
Loading at Infinity ................................... 386
10.8 Elliptic Hole Subjected to Tractions at the Hole ...... 390
10.9 Anisotropic Elliptic Body ............................. 392
10.10 Green's Functions for an Elliptic Inclusion .......... 399
11 ANISOTROPIC MEDIA WITH A CRACK OR A RIGID LINE INCLUSION ... 409
11.1 A Rigid Line Inclusion ................................ 410
11.2 Green's Functions for a Rigid Line or a Crack ......... 413
11.3 A Rigid Line Subjected to Uniform Loading ............. 417
11.4 A Crack in a Homogeneous Medium ....................... 420
11.5 Non-Oscillatory Solution for an Interfacial Crack ..... 424
11.6 Oscillatory Solution for an Interfacial Crack ......... 426
11.7 Multiple Interfacial Cracks With Nonuniform
Tractions ............................................. 431
11.8 The Comninou Crack .................................... 433
12 STEADY STATE MOTION AND SURFACE WAVES
12.1 Reduction to Elastostatics Equations .................. 440
12.2 The Stroh Formalism ................................... 441
12.3 Identities for υ < and the Airy Function χ ......... 142
5.5 Orthogonality and Closure Relations ................... 144
5.6 Positive Definite Hermitian Matrices .................. 147
5.7 The Matrix Differential Equation ...................... 149
5.8 Physical Meanings of p, α, and b ...................... 152
5.9 Nonsemisimple N ....................................... 153
5.10 Dependence of Solutions on Elastic Constants ......... 156
5.11 A.N. Stroh (1926-1962) ............................... 159
6 THE STRUCTURES AND IDENTITIES OF THE ELASTICITY MATRICES
6.1 The Structure of Nj ................................... 164
6.2 The Structure of Nj(-1) ................................ 168
6.3 Explicit Expressions of A and B ....................... 170
6.4 Explicit Expressions of S, H, and L ................... 172
6.5 Identities Relating S, H, and L ....................... 175
6.6 The Structure of S, H, and L .......................... 179
6.7 Classification of the Eigenvectors ej and ej .......... 186
6.8 Commutative 6x6 Matrices .............................. 194
6.9 Identities Connecting p, A, and В to Real Matrices .... 196
6.10 Eigenvectors of the Extraordinary Semisimple Matrix
N ..................................................... 199
7 TRANSFORMATION OF THE ELASTICITY MATRICES AND DUAL
COORDINATE SYSTEMS
7.1 Eigenvalues p(θ) ...................................... 201
7.2 Elasticity Matrices in a Rotated Coordinate System .... 207
7.3 Sextic Formalism in Dual Coordinate Systems ........... 210
7.4 Nonsemisimple N(θ) .................................... 215
7.5 Properties of N(θ) and Nj(θ) .......................... 218
7.6 The Barnett-Lothe Integral Formalism .................. 222
7.7 Invariants of S, H, and L ............................. 224
7.8 Commutative 6x6 Matrices .............................. 228
7.9 Identities Connecting A, B, and ƒ(z) to Real
Matrices .............................................. 230
7.10 General Solutions and Identities in Dual Coordinate
Systems ............................................... 235
7.11 The Tensors G1(θ) and G3(θ) ........................... 240
8 GREENS FUNCTIONS FOR INFINITE SPACE, HALF-SPACE, AND
COMPOSITE SPACE
8.1 Line Force and Line Dislocation in Infinite Space ..... 243
8.2 One-Component Green's Functions ....................... 250
8.3 Physical Meanings of the Eigenvectors ej and ej ....... 252
8.4 Interaction of Two Line Dislocations .................. 255
8.5 Surface Green's Function .............................. 258
8.6 Green's Functions for Half-Space ...................... 260
8.7 Image Singularities ................................... 268
8.8 Interfacial Green's Function .......................... 273
8.9 Green's Function for Bimaterials ...................... 283
8.10 Composite Space and Composite Wedge ................... 291
8.11 Angularly Inhomogeneous Space and Wedge ............... 295
8.12 Green's Functions for Concentrated Couple, Double
Force, and Other Higher Order Singularities ........... 298
8.13 Wedge Under a Concentrated Couple ..................... 311
9 PARTICULAR SOLUTIONS, STRESS SINGULARITIES, AND STRESS
DECAY
9.1 Wedge Subjected to Tractions .......................... 316
9.2 Nonuniform Stress Solutions in a Wedge ................ 320
9.3 Solutions for Critical Wedge Angles ................... 325
9.4 Eigenfunctions for a Wedge ............................ 329
9.5 Stress Singularities for Wedge Angles к and In ........ 337
9.6 Stress Singularities at an Interfacial Crack .......... 341
9.7 Singularities of the Form rδ(lnr)n .................... 348
9.8 Singularities Due to Curved Boundaries ................ 352
9.9 Existence of a Singularity ............................ 356
9.10 Stress Decay in an Anisotropic Elastic Strip .......... 357
10 ANISOTROPIC MATERIALS WITH AN ELLIPTIC BOUNDARY
10.1 A Force Applied to an Elliptic Rigid Inclusion ........ 365
10.2 A Moment Applied to an Elliptic Rigid Inclusion ....... 369
10.3 Green's Functions for Elliptic Hole or Rigid
Inclusion ............................................. 371
10.4 Surface Green's Function for an Elliptic Hole ......... 376
10.5 Representations of a Uniform Stress Solution .......... 378
10.6 Elliptic Hole or Rigid Inclusion Subjected to
a Uniform Loading at Infinity ......................... 380
10.7 Elliptic Elastic Inclusion Subjected to a Uniform
Loading at Infinity ................................... 386
10.8 Elliptic Hole Subjected to Tractions at the Hole ...... 390
10.9 Anisotropic Elliptic Body ............................. 392
10.10 Green's Functions for an Elliptic Inclusion .......... 399
11 ANISOTROPIC MEDIA WITH A CRACK OR A RIGID LINE INCLUSION ... 409
11.1 A Rigid Line Inclusion ................................ 410
11.2 Green's Functions for a Rigid Line or a Crack ......... 413
11.3 A Rigid Line Subjected to Uniform Loading ............. 417
11.4 A Crack in a Homogeneous Medium ....................... 420
11.5 Non-Oscillatory Solution for an Interfacial Crack ..... 424
11.6 Oscillatory Solution for an Interfacial Crack ......... 426
11.7 Multiple Interfacial Cracks With Nonuniform
Tractions ............................................. 431
11.8 The Comninou Crack .................................... 433
12 STEADY STATE MOTION AND SURFACE WAVES
12.1 Reduction to Elastostatics Equations .................. 440
12.2 The Stroh Formalism ................................... 441
12.3 Identities for υ < 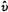 .................................. 446
12.4 Properties of A, B, and L(v) .......................... 449
12.5 Steady Motion of a Line Singularity ................... 453
12.6 Homogeneous Plane Waves or Body Waves ................. 454
12.7 Limiting Wave Speed .................................. 446
12.4 Properties of A, B, and L(v) .......................... 449
12.5 Steady Motion of a Line Singularity ................... 453
12.6 Homogeneous Plane Waves or Body Waves ................. 454
12.7 Limiting Wave Speed 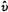 and Exceptional Waves ........... 459
12.8 One-Component Surface Waves ........................... 462
12.9 Surface Waves and Interfacial Waves ................... 468
12.10 Secular Equation and S(υ), H(υ), L(υ) for
Orthotopic Materials .................................. 477
12.11 Semisimple and Extraordinary Semisimple Matrix
N(υ) .................................................. 483
13 DEGENERATE AND NEAR DEGENERATE MATERIALS
13.1 General Solution for Degenerate and Near Degenerate
Materials ............................................. 486
13.2 Orthogonality and Closure Relations ................... 489
13.3 A Crack in a Degenerate Material ...................... 492
13.4 Conversion of Solutions from Non-Degenerate
Materials ............................................. 493
14 GENERALIZATION OF THE STROH FORMALISM
14.1 The Stroh Formalism for General Boundary
Conditions ............................................ 497
14.2 Green's Function for Half-Space for a General
Boundary Condition .................................... 502
14.3 Thermo-Anisotropic Elasticity ......................... 506
14.4 Piezoelectric Materials ............................... 511
15 THREE-DIMENSIONAL DEFORMATIONS
15.1 Stroh's Eigenrelation for an Oblique Plane ............ 520
15.2 The Tensors S[x], H[x], L[x] .......................... 523
15.3 Green's Function for Infinite Space ................... 526
15.4 Surface Green's Function for Half-Space ............... 528
15.5 Interfacial Green's Function .......................... 530
15.6 Green's Function for Half-Space ....................... 532
15.7 Green's Function for Bimaterials ...................... 534
15.8 Remarks
REFERENCES .................................................... 537
AUTHOR INDEX .................................................. 563
SUBJECT INDEX ................................................. 567 and Exceptional Waves ........... 459
12.8 One-Component Surface Waves ........................... 462
12.9 Surface Waves and Interfacial Waves ................... 468
12.10 Secular Equation and S(υ), H(υ), L(υ) for
Orthotopic Materials .................................. 477
12.11 Semisimple and Extraordinary Semisimple Matrix
N(υ) .................................................. 483
13 DEGENERATE AND NEAR DEGENERATE MATERIALS
13.1 General Solution for Degenerate and Near Degenerate
Materials ............................................. 486
13.2 Orthogonality and Closure Relations ................... 489
13.3 A Crack in a Degenerate Material ...................... 492
13.4 Conversion of Solutions from Non-Degenerate
Materials ............................................. 493
14 GENERALIZATION OF THE STROH FORMALISM
14.1 The Stroh Formalism for General Boundary
Conditions ............................................ 497
14.2 Green's Function for Half-Space for a General
Boundary Condition .................................... 502
14.3 Thermo-Anisotropic Elasticity ......................... 506
14.4 Piezoelectric Materials ............................... 511
15 THREE-DIMENSIONAL DEFORMATIONS
15.1 Stroh's Eigenrelation for an Oblique Plane ............ 520
15.2 The Tensors S[x], H[x], L[x] .......................... 523
15.3 Green's Function for Infinite Space ................... 526
15.4 Surface Green's Function for Half-Space ............... 528
15.5 Interfacial Green's Function .......................... 530
15.6 Green's Function for Half-Space ....................... 532
15.7 Green's Function for Bimaterials ...................... 534
15.8 Remarks
REFERENCES .................................................... 537
AUTHOR INDEX .................................................. 563
SUBJECT INDEX ................................................. 567
|