Preface ....................................................... vii
List of Figures ................................................ xv
List of Tables ............................................... xxii
The Big Picture ................................................. 1
1 Modern Physics at a Glance ................................... 3
Geometry and Phase Transitions, in General .................. 15
2 Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena .................... 17
2.1 Introduction ........................................... 17
2.1.1 Evolution of the Universe: Decoupling of
the Four Fundamental Forces ..................... 18
2.1.2 Three States of Water ........................... 19
2.1.3 Spins and Magnetism ............................. 21
2.2 Modern Classification of Phase Transitions ............. 23
2.3 First-Order Phase Transitions: Solid-Liquid
Transition ............................................. 24
2.4 Second-Order Phase Transitions: Scaling and
Universality ........................................... 25
2.5 Renormalization Group .................................. 26
2.5.1 Kadanoff Picture: Coarse-Graining of Spin
Blocks .......................................... 26
2.5.2 General Formulation ............................. 28
2.5.3 Critical Exponents .............................. 31
2.5.4 Origin of Universality Class .................... 32
2.5.5 Wilsonian Picture: Momentum-Space Renormal-
ization Group ................................... 33
2.6 Mathematical Miscellanies: Semi-Group Structure and
Fixed-Point Theorems ................................... 34
2.6.1 Semi-groups ..................................... 34
2.6.2 Miscellany on Fixed-Points ...................... 35
2.7 Conclusion ............................................. 35
3 Overview of Density-Functional Theory ....................... 38
3.1 Introduction ........................................... 38
3.2 Electronic Density-Functional Theory ................... 38
3.3 Classical Density-Functional Theory .................... 42
3.4 Conclusion ............................................. 46
4 Survey of Solid Geometry and Topology ....................... 49
4.1 Introduction ........................................... 49
4.2 Lattice Symmetry Groups ................................ 50
4.3 Two-Dimensional Space Groups ........................... 53
4.3.1 Hermann-Mauguin Crystallographic Notation ....... 55
4.3.2 Orbifold notation ............................... 57
4.3.3 Why Are There Exactly 17 Wallpaper Groups? ...... 78
4.3.4 Other Aspects of Topology in Physics ............ 84
4.4 Three-Dimensional Point Groups ......................... 85
4.4.1 Face-centered Cubic (FCC) Lattices .............. 85
4.4.2 Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) Lattices .............. 88
4.4.3 A15 Lattices .................................... 89
4.5 Conceptual Framework of the Foam Model ................. 90
4.6 The Kelvin Problem and the Kepler Conjecture ........... 92
4.7 Conclusion ............................................. 97
Geometry and Phase Transitions, in Colloidal Crystals ......... 101
5 Lattice Free Energy via the Foam Model ..................... 103
5.1 Introduction .......................................... 103
5.2 Bulk Free Energy ...................................... 104
5.3 Interfacial Free Energy ............................... 109
5.3.1 Charged Colloidal Crystals ..................... 109
5.3.2 Fuzzy Colloidal Crystals ....................... 1ll
5.4 Conclusion ............................................ 112
6 Phases of Charged Colloidal Crystals ....................... 115
6.1 Introduction .......................................... 115
6.2 Phase Transitions of Charged Colloids ................. 117
6.3 Foam Analogy and Charged Colloids ..................... 119
6.4 Conclusion ........................................... 120
7 Elasticity of Colloidal Crystals ........................... 122
7.1 Introduction .......................................... 122
7.2 Foam Analogy and Cubic Elastic Constants .............. 124
7.3 Elasticity of Charged Colloidal Crystals .............. 129
7.4 Elasticity of Fuzzy Colloids .......................... 137
7.5 Conclusion ............................................ 143
Geometry and Phase Transitions, in Topologically Constrained
Polymers ...................................................... 145
8 Topologically-Constrained Polymers in Theta Solution ....... 147
8.1 Introduction .......................................... 147
8.2 O(N)-Symmetric 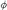 6-Theory .............................. 148
8.3 Chem-Simons Theory and Writhe ......................... 154
8.4 One-Loop Scaling of Closed Polymers ................... 159
8.5 Two-Loop Results ...................................... 163
8.6 Conclusion ............................................ 170
Summary ....................................................... 175
9 Final Thoughts ............................................. 177
Index ......................................................... 179 6-Theory .............................. 148
8.3 Chem-Simons Theory and Writhe ......................... 154
8.4 One-Loop Scaling of Closed Polymers ................... 159
8.5 Two-Loop Results ...................................... 163
8.6 Conclusion ............................................ 170
Summary ....................................................... 175
9 Final Thoughts ............................................. 177
Index ......................................................... 179
|