Preface ...................................................... xiii
Chapter 1. Quantum fields, noncommutative spaces, and motives ... 1
1 Introduction ................................................. 1
2 Basics of perturbative QFT ................................... 7
2.1 Lagrangian and Hamiltonian formalisms ................... 8
2.2 Lagrangian and the Feynman integral .................... 10
2.3 The Hamiltonian and canonical quantization ............. 11
2.4 The simplest example ................................... 13
2.5 Green's functions ...................................... 17
2.6 Wick rotation and Euclidean Green's functions .......... 18
3 Feynman diagrams ............................................ 22
3.1 The simplest case ...................................... 23
3.2 The origins of renormalization ......................... 27
3.3 Feynman graphs and rules ............................... 31
3.4 Connected Green's functions ............................ 35
3.5 The effective action and one-particle irreducible
graphs ................................................. 37
3.6 Physically observable parameters ....................... 41
3.7 The physics idea of renormalization .................... 43
4 Dimensional regularization .................................. 46
5 The graph by graph method of Bogoliubov-Parasiuk-Hepp-
Zimmermann .................................................. 52
5.1 The simplest example of subdivergence .................. 54
5.2 Superficial degree of divergence ....................... 58
5.3 Subdivergences and preparation ......................... 59
6 The Connes-Kreimer theory of perturbative renormalization ... 66
6.1 Commutative Hopf algebras and affine group schemes ..... 67
6.2 The Hopf algebra of Feynman graphs: discrete part ...... 71
6.3 The Hopf algebra of Feynman graphs: full structure ..... 78
6.4 BPHZ as a Birkhoff factorization ....................... 81
6.5 Diffeographisms and diffeomorphisms .................... 88
6.6 The renormalization group .............................. 89
7 Renormalization and the Riemann-Hilbert correspondence ...... 95
7.1 Counterterms and time-ordered exponentials ............. 96
7.2 Flat equisingular connections ......................... 103
7.3 Equivariant principal bundles and the group G* =
G 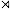 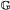 m ............................................... 114
7.4 Tannakian categories and affine group schemes ......... 119
7.5 Differential Galois theory and the local Riemann-
Hilbert correspondence ................................ 123
7.6 Universal Hopf algebra and the Riemann-Hilbert
correspondence ........................................ 128
8 Motives in a nutshell ...................................... 137
8.1 Algebraic varieties and motives ....................... 137
8.2 Pure motives .......................................... 146
8.3 Mixed motives ......................................... 151
8.4 Mixed Hodge structures ................................ 156
8.5 Tate motives, periods, and quantum fields ............. 159
9 The Standard Model of elementary particles ................. 160
9.1 Particles and interactions ............................ 162
9.2 Symmetries ............................................ 163
9.3 Quark mixing: the CKM matrix .......................... 166
9.4 The Standard Model Lagrangian ......................... 166
9.5 Quantum level: anomalies, ghosts, gauge fixing ........ 170
9.6 Massive neutrinos ..................................... 174
9.7 The Standard Model minimally coupled to gravity ....... 179
9.8 Higher derivative terms in gravity .................... 183
9.9 Symmetries as diffeomorphisms ......................... 184
10 The framework of (metric) noncommutative geometry .......... 186
10.1 Spectral geometry ..................................... 187
10.2 Spectral triples ...................................... 190
10.3 The real part of a real spectral triple ............... 192
10.4 Hochschild and cyclic cohomology ...................... 193
10.5 The local index cocycle ............................... 198
10.6 Positivity in Hochschild cohomology and Yang-Mills
action ................................................ 201
10.7 Cyclic cohomology and Chern-Simons action ............. 202
10.8 Inner fluctuations of the metric ...................... 203
11 The spectral action principle .............................. 206
11.1 Terms in Λ2 in the spectral action and scalar
curvature ............................................. 210
11.2 Seeley-DeWitt coefficients and Gilkey's theorem ....... 216
11.3 The generalized Lichnerowicz formula .................. 217
11.4 The Einstein-Yang-Mills system ........................ 218
11.5 Scale independent terms in the spectral action ........ 223
11.6 Spectral action with dilaton .......................... 227
12 Noncommutative geometry and the Standard Model ............. 230
13 The finite noncommutative geometry ......................... 234
13.1 The subalgebra and the order one condition ............ 238
13.2 The bimodule m ............................................... 114
7.4 Tannakian categories and affine group schemes ......... 119
7.5 Differential Galois theory and the local Riemann-
Hilbert correspondence ................................ 123
7.6 Universal Hopf algebra and the Riemann-Hilbert
correspondence ........................................ 128
8 Motives in a nutshell ...................................... 137
8.1 Algebraic varieties and motives ....................... 137
8.2 Pure motives .......................................... 146
8.3 Mixed motives ......................................... 151
8.4 Mixed Hodge structures ................................ 156
8.5 Tate motives, periods, and quantum fields ............. 159
9 The Standard Model of elementary particles ................. 160
9.1 Particles and interactions ............................ 162
9.2 Symmetries ............................................ 163
9.3 Quark mixing: the CKM matrix .......................... 166
9.4 The Standard Model Lagrangian ......................... 166
9.5 Quantum level: anomalies, ghosts, gauge fixing ........ 170
9.6 Massive neutrinos ..................................... 174
9.7 The Standard Model minimally coupled to gravity ....... 179
9.8 Higher derivative terms in gravity .................... 183
9.9 Symmetries as diffeomorphisms ......................... 184
10 The framework of (metric) noncommutative geometry .......... 186
10.1 Spectral geometry ..................................... 187
10.2 Spectral triples ...................................... 190
10.3 The real part of a real spectral triple ............... 192
10.4 Hochschild and cyclic cohomology ...................... 193
10.5 The local index cocycle ............................... 198
10.6 Positivity in Hochschild cohomology and Yang-Mills
action ................................................ 201
10.7 Cyclic cohomology and Chern-Simons action ............. 202
10.8 Inner fluctuations of the metric ...................... 203
11 The spectral action principle .............................. 206
11.1 Terms in Λ2 in the spectral action and scalar
curvature ............................................. 210
11.2 Seeley-DeWitt coefficients and Gilkey's theorem ....... 216
11.3 The generalized Lichnerowicz formula .................. 217
11.4 The Einstein-Yang-Mills system ........................ 218
11.5 Scale independent terms in the spectral action ........ 223
11.6 Spectral action with dilaton .......................... 227
12 Noncommutative geometry and the Standard Model ............. 230
13 The finite noncommutative geometry ......................... 234
13.1 The subalgebra and the order one condition ............ 238
13.2 The bimodule 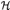 F and fermions .......................... 240
13.3 Unimodularity and hypercharges ........................ 243
13.4 The classification of Dirac operators ................. 246
13.5 Moduli space of Dirac operators and Yukawa
parameters ............................................ 252
13.6 The intersection pairing of the finite geometry ....... 255
14 The product geometry ....................................... 257
14.1 The real part of the product geometry ................. 258
15 Bosons as inner fluctuations ............................... 259
15.1 The local gauge transformations ....................... 259
15.2 Discrete part of the inner fluctuations and
the Higgs field ....................................... 260
15.3 Powers of D(0,1) ....................................... 262
15.4 Continuous part of the inner fluctuations and gauge
bosons ................................................ 265
15.5 Independence of the boson fields ...................... 269
15.6 The Dirac operator and its square ..................... 269
16 The spectral action and the Standard Model Lagrangian ...... 271
16.1 The asymptotic expansion of the spectral action on
M x F ................................................. 271
16.2 Fermionic action and Pfaffian ......................... 275
16.3 Fermion doubling, Pfaffian and Majorana fermions ...... 277
17 The Standard Model Lagrangian from the spectral action ..... 280
17.1 Change of variables in the asymptotic formula and
unification ........................................... 281
17.2 Coupling constants at unification ..................... 282
17.3 The coupling of fermions .............................. 284
17.4 The mass relation at unification ...................... 292
17.5 The see-saw mechanism ................................. 293
17.6 The mass relation and the top quark mass .............. 295
17.7 The self-interaction of the gauge bosons .............. 298
17.8 The minimal coupling of the Higgs field ............... 300
17.9 The Higgs field self-interaction ...................... 302
17.10 The Higgs scattering parameter and the Higgs mass .... 304
17.11 The gravitational terms .............................. 306
17.12 The parameters of the Standard Model ................. 308
18 Functional integral ........................................ 309
18.1 Real orientation and volume form ...................... 311
18.2 The reconstruction of spin manifolds .................. 313
18.3 Irreducible finite geometries of KO-dimension 6 ....... 314
18.4 The functional integral and open questions ............ 316
19 Dimensional regularization and noncommutative geometry ..... 318
19.1 Chiral anomalies ...................................... 318
19.2 The spaces Xz ......................................... 322
19.3 Chiral gauge transformations .......................... 325
19.4 Finiteness of anomalous graphs and relation with
residues .............................................. 326
19.5 The simplest anomalous graphs ......................... 329
19.6 Anomalous graphs in dimension 2 and the local index
cocycle ............................................... 335
Chapter 2. The Riemann zeta function and noncommutative
geometry ........................................... 341
1 Introduction ............................................... 341
2 Counting primes and the zeta function ...................... 345
3 Classical and quantum mechanics of zeta .................... 351
3.1 Spectral lines and the Riemann flow ................... 352
3.2 Symplectic volume and the scaling Hamiltonian ......... 354
3.3 Quantum system and prolate functions .................. 356
4 Principal values from the local trace formula .............. 362
4.1 Normalization of Haar measure on a modulated group .... 364
4.2 Principal values ...................................... 366
5 Quantum states of the scaling flow ......................... 370
5.1 Quantized calculus .................................... 372
5.2 Proof of Theorem 2.18 ................................. 375
6 The map C .................................................. 377
6.1 Hermite-Weber approximation and Riemann's ξ
function .............................................. 378
7 The adele class space: finitely many degrees of freedom .... 381
7.1 Geometry of the semi-local adele class space .......... 383
7.2 The Hilbert space L2(Xs) and the trace formula ........ 388
8 Weil's formulation of the explicit formulas ................ 396
8.1 L-functions ........................................... 396
8.2 Weil's explicit formula ............................... 398
8.3 Fourier transform on С F and fermions .......................... 240
13.3 Unimodularity and hypercharges ........................ 243
13.4 The classification of Dirac operators ................. 246
13.5 Moduli space of Dirac operators and Yukawa
parameters ............................................ 252
13.6 The intersection pairing of the finite geometry ....... 255
14 The product geometry ....................................... 257
14.1 The real part of the product geometry ................. 258
15 Bosons as inner fluctuations ............................... 259
15.1 The local gauge transformations ....................... 259
15.2 Discrete part of the inner fluctuations and
the Higgs field ....................................... 260
15.3 Powers of D(0,1) ....................................... 262
15.4 Continuous part of the inner fluctuations and gauge
bosons ................................................ 265
15.5 Independence of the boson fields ...................... 269
15.6 The Dirac operator and its square ..................... 269
16 The spectral action and the Standard Model Lagrangian ...... 271
16.1 The asymptotic expansion of the spectral action on
M x F ................................................. 271
16.2 Fermionic action and Pfaffian ......................... 275
16.3 Fermion doubling, Pfaffian and Majorana fermions ...... 277
17 The Standard Model Lagrangian from the spectral action ..... 280
17.1 Change of variables in the asymptotic formula and
unification ........................................... 281
17.2 Coupling constants at unification ..................... 282
17.3 The coupling of fermions .............................. 284
17.4 The mass relation at unification ...................... 292
17.5 The see-saw mechanism ................................. 293
17.6 The mass relation and the top quark mass .............. 295
17.7 The self-interaction of the gauge bosons .............. 298
17.8 The minimal coupling of the Higgs field ............... 300
17.9 The Higgs field self-interaction ...................... 302
17.10 The Higgs scattering parameter and the Higgs mass .... 304
17.11 The gravitational terms .............................. 306
17.12 The parameters of the Standard Model ................. 308
18 Functional integral ........................................ 309
18.1 Real orientation and volume form ...................... 311
18.2 The reconstruction of spin manifolds .................. 313
18.3 Irreducible finite geometries of KO-dimension 6 ....... 314
18.4 The functional integral and open questions ............ 316
19 Dimensional regularization and noncommutative geometry ..... 318
19.1 Chiral anomalies ...................................... 318
19.2 The spaces Xz ......................................... 322
19.3 Chiral gauge transformations .......................... 325
19.4 Finiteness of anomalous graphs and relation with
residues .............................................. 326
19.5 The simplest anomalous graphs ......................... 329
19.6 Anomalous graphs in dimension 2 and the local index
cocycle ............................................... 335
Chapter 2. The Riemann zeta function and noncommutative
geometry ........................................... 341
1 Introduction ............................................... 341
2 Counting primes and the zeta function ...................... 345
3 Classical and quantum mechanics of zeta .................... 351
3.1 Spectral lines and the Riemann flow ................... 352
3.2 Symplectic volume and the scaling Hamiltonian ......... 354
3.3 Quantum system and prolate functions .................. 356
4 Principal values from the local trace formula .............. 362
4.1 Normalization of Haar measure on a modulated group .... 364
4.2 Principal values ...................................... 366
5 Quantum states of the scaling flow ......................... 370
5.1 Quantized calculus .................................... 372
5.2 Proof of Theorem 2.18 ................................. 375
6 The map C .................................................. 377
6.1 Hermite-Weber approximation and Riemann's ξ
function .............................................. 378
7 The adele class space: finitely many degrees of freedom .... 381
7.1 Geometry of the semi-local adele class space .......... 383
7.2 The Hilbert space L2(Xs) and the trace formula ........ 388
8 Weil's formulation of the explicit formulas ................ 396
8.1 L-functions ........................................... 396
8.2 Weil's explicit formula ............................... 398
8.3 Fourier transform on С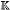 .............................. 399
8.4 Computation of the principal values ................... 400
8.5 Reformulation of the explicit formula ................. 406
9 Spectral realization of critical zeros of L-functions ...... 407
9.1 L-functions and homogeneous distributions on .............................. 399
8.4 Computation of the principal values ................... 400
8.5 Reformulation of the explicit formula ................. 406
9 Spectral realization of critical zeros of L-functions ...... 407
9.1 L-functions and homogeneous distributions on 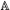 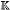 ...... 409
9.2 Approximate units in the Sobolev spaces L2δ(C ...... 409
9.2 Approximate units in the Sobolev spaces L2δ(C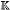 ) ....... 414
9.3 Proof of Theorem 2.47 ................................. 416
10 A Lefschetz formula for Archimedean local factors .......... 421
10.1 Archimedean local L-factors ........................... 422
10.2 Asymptotic form of the number of zeros of
L-functions ........................................... 423
10.3 Weil form of logarithmic derivatives of local
factors ............................................... 424
10.4 Lefschetz formula for complex places .................. 427
10.5 Lefschetz formula for real places ..................... 428
10.6 The question of the spectral realization .............. 431
10.7 Local factors for curves .............................. 434
10.8 Analogy with dimensional regularization ............... 435
Chapter 3. Quantum statistical mechanics and Galois
symmetries ......................................... 437
1 Overview: three systems .................................... 437
2 Quantum statistical mechanics .............................. 442
2.1 Observables and time evolution ........................ 444
2.2 The KMS condition ..................................... 445
2.3 Symmetries ............................................ 449
2.4 Warming up and cooling down ........................... 451
2.5 Pushforward of KMS states ............................. 451
3 ) ....... 414
9.3 Proof of Theorem 2.47 ................................. 416
10 A Lefschetz formula for Archimedean local factors .......... 421
10.1 Archimedean local L-factors ........................... 422
10.2 Asymptotic form of the number of zeros of
L-functions ........................................... 423
10.3 Weil form of logarithmic derivatives of local
factors ............................................... 424
10.4 Lefschetz formula for complex places .................. 427
10.5 Lefschetz formula for real places ..................... 428
10.6 The question of the spectral realization .............. 431
10.7 Local factors for curves .............................. 434
10.8 Analogy with dimensional regularization ............... 435
Chapter 3. Quantum statistical mechanics and Galois
symmetries ......................................... 437
1 Overview: three systems .................................... 437
2 Quantum statistical mechanics .............................. 442
2.1 Observables and time evolution ........................ 444
2.2 The KMS condition ..................................... 445
2.3 Symmetries ............................................ 449
2.4 Warming up and cooling down ........................... 451
2.5 Pushforward of KMS states ............................. 451
3 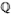 -lattices and commensurability ............................ 452
4 1-dimensional -lattices and commensurability ............................ 452
4 1-dimensional 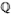 -lattices ................................... 454
4.1 The Bost-Connes system ................................ 458
4.2 Hecke algebras ........................................ 459
4.3 Symmetries of the ВС system ........................... 461
4.4 The arithmetic subalgebra ............................. 462
4.5 Class field theory and the Kronecker-Weber theorem .... 470
4.6 KMS states and class field theory ..................... 474
4.7 The class field theory problem: algebras and fields ... 476
4.8 The Shimura variety of -lattices ................................... 454
4.1 The Bost-Connes system ................................ 458
4.2 Hecke algebras ........................................ 459
4.3 Symmetries of the ВС system ........................... 461
4.4 The arithmetic subalgebra ............................. 462
4.5 Class field theory and the Kronecker-Weber theorem .... 470
4.6 KMS states and class field theory ..................... 474
4.7 The class field theory problem: algebras and fields ... 476
4.8 The Shimura variety of 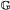 m ............................. 479
4.9 QSM and QFT of 1-dimensional m ............................. 479
4.9 QSM and QFT of 1-dimensional 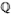 -lattices ............... 481
5 2-dimensional -lattices ............... 481
5 2-dimensional 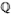 -lattices ................................... 483
5.1 Elliptic curves and Tate modules ...................... 486
5.2 Algebras and groupoids ................................ 488
5.3 Time evolution and regular representation ............. 493
5.4 Symmetries ............................................ 495
6 The modular field .......................................... 501
6.1 The modular field of level N = 1 ...................... 502
6.2 Modular-field of level N .............................. 504
6.3 Modular functions and modular forms ................... 511
6.4 Explicit computations for N = 2 and N = 4 ............. 513
6.5 The modular field F and -lattices ................................... 483
5.1 Elliptic curves and Tate modules ...................... 486
5.2 Algebras and groupoids ................................ 488
5.3 Time evolution and regular representation ............. 493
5.4 Symmetries ............................................ 495
6 The modular field .......................................... 501
6.1 The modular field of level N = 1 ...................... 502
6.2 Modular-field of level N .............................. 504
6.3 Modular functions and modular forms ................... 511
6.4 Explicit computations for N = 2 and N = 4 ............. 513
6.5 The modular field F and 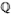 -lattices ................... 514
7 Arithmetic of the GL2 system ............................... 518
7.1 The arithmetic subalgebra: explicit elements .......... 518
7.2 The arithmetic subalgebra: definition ................. 521
7.3 Division relations in the arithmetic algebra .......... 527
7.4 KMS states ............................................ 532
7.5 Action of symmetries on KMS states .................... 541
7.6 Low-temperature KMS states and Galois action .......... 542
7.7 The high temperature range ............................ 543
7.8 The Shimura variety of GL2 ............................ 545
7.9 The noncommutative boundary of modular curves ......... 546
7.10 Compatibility between the systems ..................... 549
8 KMS states and complex multiplication ...................... 551
8.1 1-dimensional -lattices ................... 514
7 Arithmetic of the GL2 system ............................... 518
7.1 The arithmetic subalgebra: explicit elements .......... 518
7.2 The arithmetic subalgebra: definition ................. 521
7.3 Division relations in the arithmetic algebra .......... 527
7.4 KMS states ............................................ 532
7.5 Action of symmetries on KMS states .................... 541
7.6 Low-temperature KMS states and Galois action .......... 542
7.7 The high temperature range ............................ 543
7.8 The Shimura variety of GL2 ............................ 545
7.9 The noncommutative boundary of modular curves ......... 546
7.10 Compatibility between the systems ..................... 549
8 KMS states and complex multiplication ...................... 551
8.1 1-dimensional 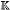 -lattices .............................. 551
8.2 K-lattices and -lattices .............................. 551
8.2 K-lattices and 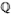 -lattices ............................. 553
8.3 Adelic description of -lattices ............................. 553
8.3 Adelic description of 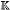 -lattices ...................... 554
8.4 Algebra and time evolution ............................ 556
8.5 K-lattices and ideals ................................. 558
8.6 Arithmetic subalgebra ................................. 559
8.7 Symmetries ............................................ 560
8.8 Low-temperature KMS states and Galois action .......... 563
8.9 High temperature KMS states ........................... 569
8.10 Comparison with other systems ......................... 572
9 Quantum statistical mechanics of Shimura varieties ......... 574
Chapter 4. Endomotives, thermodynamics, and the Weil
explicit formula ................................... 577
1 Morphisms and categories of noncommutative spaces .......... 577
1.1 The КК-category ....................................... 582
1.2 The cyclic category ................................... 585
1.3 The non-unital case ................................... 588
1.4 Cyclic (co)homology ................................... 589
2 Endomotives ................................................ 591
2.1 Algebraic endomotives ................................. 594
2.2 Analytic endomotives .................................. 598
2.3 Galois action ......................................... 600
2.4 Uniform systems and measured endomotives .............. 603
2.5 Compatibility of endomotives categories ............... 604
2.6 Self-maps of algebraic varieties ...................... 606
2.7 The Bost Connes endomotive ............................ 607
3 Motives and noncommutative spaces: higher dimensional
perspectives ............................................... 610
3.1 Geometric correspondences ............................. 610
3.2 Algebraic cycles and K-theory ......................... 612
4 A thermodynamic "Frobenius" in characteristic zero ......... 615
4.1 Tomita's theory and the modular automorphism group .... 616
4.2 Regular extremal KMS states (cooling) ................. 618
4.3 The dual system ....................................... 622
4.4 Field extensions and duality of factors
(an analogy) .......................................... 623
4.5 Low temperature KMS states and scaling ................ 626
4.6 The kernel of the dual trace .......................... 631
4.7 Holomorphic modules ................................... 634
4.8 The cooling morphism (distillation) ................... 636
4.9 Distillation of the Bost Connes endomotive ............ 638
4.10 Spectral realization .................................. 648
5 A cohomological Lefschetz trace formula .................... 650
5.1 The adele class space of a global field ............... 651
5.2 The cyclic module of the adele class space ............ 652
5.3 The restriction map to the idele class group .......... 653
5.4 The Morita equivalence and cokernel for -lattices ...................... 554
8.4 Algebra and time evolution ............................ 556
8.5 K-lattices and ideals ................................. 558
8.6 Arithmetic subalgebra ................................. 559
8.7 Symmetries ............................................ 560
8.8 Low-temperature KMS states and Galois action .......... 563
8.9 High temperature KMS states ........................... 569
8.10 Comparison with other systems ......................... 572
9 Quantum statistical mechanics of Shimura varieties ......... 574
Chapter 4. Endomotives, thermodynamics, and the Weil
explicit formula ................................... 577
1 Morphisms and categories of noncommutative spaces .......... 577
1.1 The КК-category ....................................... 582
1.2 The cyclic category ................................... 585
1.3 The non-unital case ................................... 588
1.4 Cyclic (co)homology ................................... 589
2 Endomotives ................................................ 591
2.1 Algebraic endomotives ................................. 594
2.2 Analytic endomotives .................................. 598
2.3 Galois action ......................................... 600
2.4 Uniform systems and measured endomotives .............. 603
2.5 Compatibility of endomotives categories ............... 604
2.6 Self-maps of algebraic varieties ...................... 606
2.7 The Bost Connes endomotive ............................ 607
3 Motives and noncommutative spaces: higher dimensional
perspectives ............................................... 610
3.1 Geometric correspondences ............................. 610
3.2 Algebraic cycles and K-theory ......................... 612
4 A thermodynamic "Frobenius" in characteristic zero ......... 615
4.1 Tomita's theory and the modular automorphism group .... 616
4.2 Regular extremal KMS states (cooling) ................. 618
4.3 The dual system ....................................... 622
4.4 Field extensions and duality of factors
(an analogy) .......................................... 623
4.5 Low temperature KMS states and scaling ................ 626
4.6 The kernel of the dual trace .......................... 631
4.7 Holomorphic modules ................................... 634
4.8 The cooling morphism (distillation) ................... 636
4.9 Distillation of the Bost Connes endomotive ............ 638
4.10 Spectral realization .................................. 648
5 A cohomological Lefschetz trace formula .................... 650
5.1 The adele class space of a global field ............... 651
5.2 The cyclic module of the adele class space ............ 652
5.3 The restriction map to the idele class group .......... 653
5.4 The Morita equivalence and cokernel for 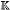 = = 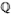 ........ 654
5.5 The cokernel of p for general global fields ........... 656
5.6 Trace pairing and vanishing ........................... 670
5.7 Weil's explicit formula as a trace formula ............ 671
5.8 Weil positivity and the Riemann Hypothesis ............ 672
6 The Weil proof for function fields ......................... 674
6.1 Function fields and their zeta functions .............. 675
6.2 Correspondences and divisors in С х С ................. 678
6.3 Frobenius correspondences and effective divisors ...... 680
6.4 Positivity in the Weil proof .......................... 682
7 A noncommutative geometry perspective ...................... 685
7.1 Distributional trace of a flow ........................ 686
7.2 The periodic orbits of the action of С ........ 654
5.5 The cokernel of p for general global fields ........... 656
5.6 Trace pairing and vanishing ........................... 670
5.7 Weil's explicit formula as a trace formula ............ 671
5.8 Weil positivity and the Riemann Hypothesis ............ 672
6 The Weil proof for function fields ......................... 674
6.1 Function fields and their zeta functions .............. 675
6.2 Correspondences and divisors in С х С ................. 678
6.3 Frobenius correspondences and effective divisors ...... 680
6.4 Positivity in the Weil proof .......................... 682
7 A noncommutative geometry perspective ...................... 685
7.1 Distributional trace of a flow ........................ 686
7.2 The periodic orbits of the action of С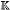 on X on X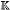 ........ 690
7.3 Frobenius (scaling) correspondence and the trace
formula ............................................... 691
7.4 The Fubini theorem and trivial correspondences ........ 693
7.5 The curve inside the adele class space ................ 694
7.6 Vortex configurations (an analogy) .................... 712
7.7 Building a dictionary ................................. 721
8 The analogy between QG and RH .............................. 723
8.1 KMS states and the electroweak phase transition ....... 723
8.2 Observables in QG ..................................... 727
8.3 Invertibility at low temperature ...................... 729
8.4 Spectral correspondences .............................. 730
8.5 Spectral cobordisms ................................... 730
8.6 Scaling action ........................................ 730
8.7 Moduli spaces for ........ 690
7.3 Frobenius (scaling) correspondence and the trace
formula ............................................... 691
7.4 The Fubini theorem and trivial correspondences ........ 693
7.5 The curve inside the adele class space ................ 694
7.6 Vortex configurations (an analogy) .................... 712
7.7 Building a dictionary ................................. 721
8 The analogy between QG and RH .............................. 723
8.1 KMS states and the electroweak phase transition ....... 723
8.2 Observables in QG ..................................... 727
8.3 Invertibility at low temperature ...................... 729
8.4 Spectral correspondences .............................. 730
8.5 Spectral cobordisms ................................... 730
8.6 Scaling action ........................................ 730
8.7 Moduli spaces for  -lattices and spectral
correspondences ....................................... 731
Appendix ...................................................... 733
1 Operator algebras .......................................... 733
1.1 C*-algebras ........................................... 733
1.2 Von Neumann algebras .................................. 734
1.3 The passing of time ................................... 738
2 Galois theory .............................................. 741
Bibliography .................................................. 749
Index ......................................................... 763 -lattices and spectral
correspondences ....................................... 731
Appendix ...................................................... 733
1 Operator algebras .......................................... 733
1.1 C*-algebras ........................................... 733
1.2 Von Neumann algebras .................................. 734
1.3 The passing of time ................................... 738
2 Galois theory .............................................. 741
Bibliography .................................................. 749
Index ......................................................... 763
|