Preface ........................................................ xv
1. Introduction ................................................. 1
1.1. Calculus of Variations, PDEs and Quasiconformal
Mappings ................................................ 2
1.2. Degeneracy .............................................. 6
1.3. Holomorphic Dynamical Systems ........................... 8
1.4. Elliptic Operators and the Beurling Transform ........... 9
2. A Background in Conformal Geometry .......................... 12
2.1. Matrix Fields and Conformal Structures ................. 12
2.2. The Hyperbolic Metric .................................. 15
2.3. The Space S(2) ......................................... 17
2.4. The Linear Distortion .................................. 21
2.5. Quasiconformal Mappings ................................ 22
2.6. Radial Stretchings ..................................... 28
2.7. Hausdorff Dimension .................................... 30
2.8. Degree and Jacobian .................................... 32
2.9. A Background in Complex Analysis ....................... 34
2.9.1. Analysis with Complex Notation .................. 34
2.9.2. Riemann Mapping Theorem and Uniformization ...... 36
2.9.3. Schwarz-Pick Lemma of Ahlfors ................... 37
2.9.4. Normal Families and Montel's Theorem ............ 39
2.9.5. Hurwitz's Theorem ............................... 40
2.9.6. Bloch's Theorem ................................. 40
2.9.7. The Argument Principle .......................... 41
2.10.Distortion by Conformal Mapping ........................... 41
2.10.1.The Area Formula ................................ 41
2.10.2.Koebe 1-Theorem and Distortion Theorem .......... 44
4
3. The Foundations of Quasiconformal Mappings .................. 48
3.1. Basic Properties ....................................... 48
3.2. Quasisymmetry .......................................... 49
3.3. The Gehring-Lehto Theorem .............................. 51
3.3.1. The Differentiability of Open Mappings .......... 52
3.4. Quasisymmetric Maps Are Quasiconformal ................. 58
3.5. Global Quasiconformal Maps Are Quasisymmetric .......... 64
3.6. Quasiconformality and Quasisymmetry: Local
Equivalence ............................................ 70
3.7. Lusin's Condition 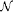 and Positivity of the Jacobian .... 72
3.8. Change of Variables .................................... 76
3.9. Quasisymmetry and Equicontinuity ....................... 78
3.10.Holder Regularity ...................................... 80
3.11.Quasisymmetry and δ-Monotone Mappings .................. 83
4. Complex Potentials .......................................... 92
4.1. The Fourier Transform .................................. 98
4.1.1. The Fourier Transform in L1 and L2 .............. 99
4.1.2. Fourier Transform on Measures .................. 100
4.1.3. Multipliers .................................... 100
4.1.4. The Hecke Identities ........................... 101
4.2. The Complex Riesz Transforms Rk ....................... 102
4.2.1. Potentials Associated with Rk .................. 103
4.3. Quantitative Analysis of Complex Potentials ........... 104
4.3.1. The Logarithmic Potential ...................... 105
4.3.2. The Cauchy Transform ........................... 109
4.4. Maximal Functions and Interpolation ................... 117
4.4.1. Interpolation .................................. 117
4.4.2. Maximal Functions .............................. 120
4.5. Weak-Type Estimates and LP-Bounds ..................... 124
4.5.1. Weak-Type Estimates for Complex Riesz
Transforms ..................................... 124
4.5.2. Estimates for the Beurling Transform S ......... 128
4.5.3. Weighted LP-Theory for S ...................... 130
4.6. BMO and the Beurling Transform ........................ 131
4.6.1. Global John-Nirenberg Inequalities ............. 132
4.6.2. Norm Bounds in BMO ............................. 134
4.6.3. Orthogonality Properties of S .................. 135
4.6.4. Proof of the Pointwise Estimates ............... 137
4.6.5. Commutators .................................... 143
4.6.6. The Beurling Transform of Characteristic
Functions ...................................... 146
4.7. Holder Estimates ...................................... 147
4.7.1. Holder Bounds for the Beurling Transform ....... 147
4.7.2. The Inhomogeneous Cauchy-Riemann Equation ...... 149
4.8. Beurling Transforms for Boundary Value Problems ....... 150
4.8.1. The Beurling Transform on Domains .............. 151
4.8.2. LP-Theory ...................................... 153
4.8.3. Complex Potentials for the Dirichlet Problem ... 155
4.9. Complex Potentials in Multiply Connected Domains ...... 158
5. The Measurable Riemann Mapping Theorem: The Existence
Theory of Quasiconformal Mappings .......................... 161
5.1. The Basic Beltrami Equation ........................... 163
5.2. Quasiconformal Mappings with Smooth Beltrami
Coefficient ........................................... 165
5.3. The Measurable Riemann Mapping Theorem ................ 168
5.4. LP-Estimates and the Critical Interval ................ 172
5.4.1. The Caccioppoli Inequalities ................... 174
5.4.2. Weakly Quasiregular Mappings ................... 178
5.5. Stoilow Factorization ................................. 178
5.6. Factoring with Small Distortion ....................... 184
5.7. Analytic Dependence on Parameters ..................... 185
5.8. Extension of Quasisymmetric Mappings of the Real
Line .................................................. 189
5.8.1. The Douady-Earle Extension ..................... 191
5.8.2. The Beurling-Ahlfors Extension ................. 192
5.9. Reflection ............................................ 192
5.10.Conformed Welding ..................................... 193
6. Parameterizing General Linear Elliptic Systems ............. 195
6.1. Stoilow Factorization for General Elliptic Systems .... 196
6.2. Linear Families of Quasiconformal Mappings ............ 198
6.3. The Reduced Beltrami Equation ......................... 202
6.4. Homeomorphic Solutions to Reduced Equations ........... 204
6.4.1. Fabes-Stroock Theorem .......................... 206
7. The Concept of Ellipticity ................................. 210
7.1. The Algebraic Concept of Ellipticity .................. 211
7.2. Some Examples of First-Order Equations ................ 213
7.3. General Elliptic First-Order Operators in Two
Variables ............................................. 214
7.3.1. Complexification ............................... 215
7.3.2. Homotopy Classification ........................ 217
7.3.3. Classification; n = 1 .......................... 217
7.4. Partial Differential Operators with Measurable
Coefficients .......................................... 221
7.5. Quasilinear Operators ................................. 222
7.6. Lusin Measurability ................................... 223
7.7. Fully Nonlinear Equations ............................. 226
7.8. Second-Order Elliptic Systems ......................... 231
7.8.1. Measurable Coefficients ........................ 233
8.Solving General Nonlinear First-Order Elliptic Systems ...... 235
8.1. Equations Without Principal Solutions ................. 236
8.2. Existence of Solutions ................................ 237
8.3. Proof of Theorem 8.2.1 ................................ 239
8.3.1. Step 1: H Continuous, Supported on an
Annulus ........................................ 239
8.3.2. Step 2: Good Smoothing of Н .................... 242
8.3.3. Step 3: Lusin-Egoroff Convergence .............. 244
8.3.4. Step 4: Passing to the Limit ................... 246
8.4. Equations with Infinitely Many Principal Solutions .... 248
8.5. Liouville Theorems .................................... 249
8.6. Uniqueness ............................................ 253
8.6.1. Uniqueness for Normalized Solutions ............ 255
8.7. Lipschitz H(z,ω,ζ) .................................... 256
9.Nonlinear Riemann Mapping Theorems .......................... 259
9.1. Ellipticity and Change of Variables ................... 261
9.2. The Nonlinear Mapping Theorem: Simply Connected
Domains ............................................... 263
9.2.1.Existence ....................................... 264
9.2.2.Uniqueness ...................................... 267
9.3. Mappings onto Multiply Connected Schottky Domains ..... 269
9.3.1. Some Preliminaries ............................. 271
9.3.2. Proof of the Mapping Theorem 9.3.4 ............. 273
10.Conformal Deformations and Beltrami Systems ................ 275
10.1.Quasilinearity of the Beltrami System ................. 275
10.1.1.The Complex Equation ........................... 276
10.2.Conformal Equivalence of Riemannian Structures ........ 279
10.3.Group Properties of Solutions ......................... 280
10.3.1.Semigroups ..................................... 283
10.3.2.Sullivan-Tukia Theorem ......................... 285
10.3.3.Ellipticity Constants .......................... 287
11.A Quasilinear Cauchy Problem ............................... 289
11.1.The Nonlinear and Positivity of the Jacobian .... 72
3.8. Change of Variables .................................... 76
3.9. Quasisymmetry and Equicontinuity ....................... 78
3.10.Holder Regularity ...................................... 80
3.11.Quasisymmetry and δ-Monotone Mappings .................. 83
4. Complex Potentials .......................................... 92
4.1. The Fourier Transform .................................. 98
4.1.1. The Fourier Transform in L1 and L2 .............. 99
4.1.2. Fourier Transform on Measures .................. 100
4.1.3. Multipliers .................................... 100
4.1.4. The Hecke Identities ........................... 101
4.2. The Complex Riesz Transforms Rk ....................... 102
4.2.1. Potentials Associated with Rk .................. 103
4.3. Quantitative Analysis of Complex Potentials ........... 104
4.3.1. The Logarithmic Potential ...................... 105
4.3.2. The Cauchy Transform ........................... 109
4.4. Maximal Functions and Interpolation ................... 117
4.4.1. Interpolation .................................. 117
4.4.2. Maximal Functions .............................. 120
4.5. Weak-Type Estimates and LP-Bounds ..................... 124
4.5.1. Weak-Type Estimates for Complex Riesz
Transforms ..................................... 124
4.5.2. Estimates for the Beurling Transform S ......... 128
4.5.3. Weighted LP-Theory for S ...................... 130
4.6. BMO and the Beurling Transform ........................ 131
4.6.1. Global John-Nirenberg Inequalities ............. 132
4.6.2. Norm Bounds in BMO ............................. 134
4.6.3. Orthogonality Properties of S .................. 135
4.6.4. Proof of the Pointwise Estimates ............... 137
4.6.5. Commutators .................................... 143
4.6.6. The Beurling Transform of Characteristic
Functions ...................................... 146
4.7. Holder Estimates ...................................... 147
4.7.1. Holder Bounds for the Beurling Transform ....... 147
4.7.2. The Inhomogeneous Cauchy-Riemann Equation ...... 149
4.8. Beurling Transforms for Boundary Value Problems ....... 150
4.8.1. The Beurling Transform on Domains .............. 151
4.8.2. LP-Theory ...................................... 153
4.8.3. Complex Potentials for the Dirichlet Problem ... 155
4.9. Complex Potentials in Multiply Connected Domains ...... 158
5. The Measurable Riemann Mapping Theorem: The Existence
Theory of Quasiconformal Mappings .......................... 161
5.1. The Basic Beltrami Equation ........................... 163
5.2. Quasiconformal Mappings with Smooth Beltrami
Coefficient ........................................... 165
5.3. The Measurable Riemann Mapping Theorem ................ 168
5.4. LP-Estimates and the Critical Interval ................ 172
5.4.1. The Caccioppoli Inequalities ................... 174
5.4.2. Weakly Quasiregular Mappings ................... 178
5.5. Stoilow Factorization ................................. 178
5.6. Factoring with Small Distortion ....................... 184
5.7. Analytic Dependence on Parameters ..................... 185
5.8. Extension of Quasisymmetric Mappings of the Real
Line .................................................. 189
5.8.1. The Douady-Earle Extension ..................... 191
5.8.2. The Beurling-Ahlfors Extension ................. 192
5.9. Reflection ............................................ 192
5.10.Conformed Welding ..................................... 193
6. Parameterizing General Linear Elliptic Systems ............. 195
6.1. Stoilow Factorization for General Elliptic Systems .... 196
6.2. Linear Families of Quasiconformal Mappings ............ 198
6.3. The Reduced Beltrami Equation ......................... 202
6.4. Homeomorphic Solutions to Reduced Equations ........... 204
6.4.1. Fabes-Stroock Theorem .......................... 206
7. The Concept of Ellipticity ................................. 210
7.1. The Algebraic Concept of Ellipticity .................. 211
7.2. Some Examples of First-Order Equations ................ 213
7.3. General Elliptic First-Order Operators in Two
Variables ............................................. 214
7.3.1. Complexification ............................... 215
7.3.2. Homotopy Classification ........................ 217
7.3.3. Classification; n = 1 .......................... 217
7.4. Partial Differential Operators with Measurable
Coefficients .......................................... 221
7.5. Quasilinear Operators ................................. 222
7.6. Lusin Measurability ................................... 223
7.7. Fully Nonlinear Equations ............................. 226
7.8. Second-Order Elliptic Systems ......................... 231
7.8.1. Measurable Coefficients ........................ 233
8.Solving General Nonlinear First-Order Elliptic Systems ...... 235
8.1. Equations Without Principal Solutions ................. 236
8.2. Existence of Solutions ................................ 237
8.3. Proof of Theorem 8.2.1 ................................ 239
8.3.1. Step 1: H Continuous, Supported on an
Annulus ........................................ 239
8.3.2. Step 2: Good Smoothing of Н .................... 242
8.3.3. Step 3: Lusin-Egoroff Convergence .............. 244
8.3.4. Step 4: Passing to the Limit ................... 246
8.4. Equations with Infinitely Many Principal Solutions .... 248
8.5. Liouville Theorems .................................... 249
8.6. Uniqueness ............................................ 253
8.6.1. Uniqueness for Normalized Solutions ............ 255
8.7. Lipschitz H(z,ω,ζ) .................................... 256
9.Nonlinear Riemann Mapping Theorems .......................... 259
9.1. Ellipticity and Change of Variables ................... 261
9.2. The Nonlinear Mapping Theorem: Simply Connected
Domains ............................................... 263
9.2.1.Existence ....................................... 264
9.2.2.Uniqueness ...................................... 267
9.3. Mappings onto Multiply Connected Schottky Domains ..... 269
9.3.1. Some Preliminaries ............................. 271
9.3.2. Proof of the Mapping Theorem 9.3.4 ............. 273
10.Conformal Deformations and Beltrami Systems ................ 275
10.1.Quasilinearity of the Beltrami System ................. 275
10.1.1.The Complex Equation ........................... 276
10.2.Conformal Equivalence of Riemannian Structures ........ 279
10.3.Group Properties of Solutions ......................... 280
10.3.1.Semigroups ..................................... 283
10.3.2.Sullivan-Tukia Theorem ......................... 285
10.3.3.Ellipticity Constants .......................... 287
11.A Quasilinear Cauchy Problem ............................... 289
11.1.The Nonlinear 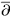 -Equation .............................. 289
11.2.A Fixed-Point Theorem ................................. 290
11.3.Existence and Uniqueness .............................. 291
12.Holomorphic Motions ........................................ 293
12.1.The λ-Lemma ........................................... 294
12.2.Two Compelling Examples ............................... 296
12.2.1.Limit Sets of Kleinian Groups .................. 296
12.2.2.Julia Sets of Rational Maps .................... 297
12.3.The Extended λ-Lemma .................................. 298
12.3.1.Holomorphic Motions and the Cauchy Problem ..... 299
12.3.2.Holomorphic Axiom of Choice .................... 300
12.4.Distortion of Dimension in Holomorphic Motions ........ 306
12.5.Embedding Quasiconformal Mappings in Holomorphic
Flows ................................................. 309
12.6.Distortion Theorems ................................... 310
12.7.Deformations of Quasiconformal Mappings ............... 313
13.Higher Integrability ....................................... 316
13.1.Distortion of Area .................................... 317
13.1.1.Initial Bounds for Distortion of Area .......... 318
13.1.2.Weighted Area Distortion ....................... 319
13.1.3.An Example ..................................... 323
13.1.4.General Area Estimates ......................... 324
13.2.Higher Integrability .................................. 327
13.2.1.Integrability at the Borderline ................ 330
13.2.2.Distortion of Hausdorff Dimension .............. 332
13.3.The Dimension of Quasicircles ......................... 333
13.3.1.Symmetrization of Beltrami Coefficients ........ 336
13.3.2.Distortion of Dimension ........................ 338
13.4.Quasiconformal Mappings and BMO ....................... 343
13.4.1.Quasiconformal Jacobians and Ар-Weights ........ 345
13.5.Painleve's Theorem: Removable Singularities ........... 347
13.5.1.Distortion of Hausdorff Measure ................ 351
13.6.Examples of Nonremovable Sets ......................... 357
14.LP-Theory of Beltrami Operators ............................ 362
14.1.Spectral Bounds and Linear Beltrami Operators ......... 365
14.2.Invertibility of the Beltrami Operators ............... 366
14.2.1.Proof of Invertibility; Theorem 14.0.4 ......... 368
14.3.Determining the Critical Interval ..................... 369
14.4.Injectivity in the Borderline Cases ................... 373
14.4.1.Failure of Factorization in W1,q ................ 376
14.4.2.Injectivity and Liouville-Type Theorems ........ 378
14.5.Beltrami Operators; Coefficients in VMO ............... 382
14.6.Bounds for the Beurling Transform ..................... 385
15.Schauder Estimates for Beltrami Operators .................. 389
15.1.Examples .............................................. 390
15.2.The Beltrami Equation with Constant Coefficients ...... 391
15.3.A Partition of Unity .................................. 392
15.4.An Interpolation ...................................... 394
15.5.Hölder Regularity for Variable Coefficients ........... 395
15.6.Hölder-Caccioppoli Estimates .......................... 398
15.7.Quasilinear Equations ................................. 400
16.Applications to Partial Differential Equations ............. 403
16.1.The Hodge * Method .................................... 404
16.1.1.Equations of Divergence Type: The A-Harmonic
Operator ....................................... 405
16.1.2.The Natural Domain of Definition ............... 406
16.1.3.The Л-Harmonic Conjugate Function .............. 408
16.1.4.Regularity of Solutions ........................ 409
16.1.5.General Linear Divergence Equations ............ 411
16.1.6.А-Harmonic Fields .............................. 414
16.2.Topological Properties of Solutions ................... 418
16.3.The Hodographic Method ................................ 420
16.3.1.The Continuity Equation ........................ 420
16.3.2.The p-Harmonic Operator div| -Equation .............................. 289
11.2.A Fixed-Point Theorem ................................. 290
11.3.Existence and Uniqueness .............................. 291
12.Holomorphic Motions ........................................ 293
12.1.The λ-Lemma ........................................... 294
12.2.Two Compelling Examples ............................... 296
12.2.1.Limit Sets of Kleinian Groups .................. 296
12.2.2.Julia Sets of Rational Maps .................... 297
12.3.The Extended λ-Lemma .................................. 298
12.3.1.Holomorphic Motions and the Cauchy Problem ..... 299
12.3.2.Holomorphic Axiom of Choice .................... 300
12.4.Distortion of Dimension in Holomorphic Motions ........ 306
12.5.Embedding Quasiconformal Mappings in Holomorphic
Flows ................................................. 309
12.6.Distortion Theorems ................................... 310
12.7.Deformations of Quasiconformal Mappings ............... 313
13.Higher Integrability ....................................... 316
13.1.Distortion of Area .................................... 317
13.1.1.Initial Bounds for Distortion of Area .......... 318
13.1.2.Weighted Area Distortion ....................... 319
13.1.3.An Example ..................................... 323
13.1.4.General Area Estimates ......................... 324
13.2.Higher Integrability .................................. 327
13.2.1.Integrability at the Borderline ................ 330
13.2.2.Distortion of Hausdorff Dimension .............. 332
13.3.The Dimension of Quasicircles ......................... 333
13.3.1.Symmetrization of Beltrami Coefficients ........ 336
13.3.2.Distortion of Dimension ........................ 338
13.4.Quasiconformal Mappings and BMO ....................... 343
13.4.1.Quasiconformal Jacobians and Ар-Weights ........ 345
13.5.Painleve's Theorem: Removable Singularities ........... 347
13.5.1.Distortion of Hausdorff Measure ................ 351
13.6.Examples of Nonremovable Sets ......................... 357
14.LP-Theory of Beltrami Operators ............................ 362
14.1.Spectral Bounds and Linear Beltrami Operators ......... 365
14.2.Invertibility of the Beltrami Operators ............... 366
14.2.1.Proof of Invertibility; Theorem 14.0.4 ......... 368
14.3.Determining the Critical Interval ..................... 369
14.4.Injectivity in the Borderline Cases ................... 373
14.4.1.Failure of Factorization in W1,q ................ 376
14.4.2.Injectivity and Liouville-Type Theorems ........ 378
14.5.Beltrami Operators; Coefficients in VMO ............... 382
14.6.Bounds for the Beurling Transform ..................... 385
15.Schauder Estimates for Beltrami Operators .................. 389
15.1.Examples .............................................. 390
15.2.The Beltrami Equation with Constant Coefficients ...... 391
15.3.A Partition of Unity .................................. 392
15.4.An Interpolation ...................................... 394
15.5.Hölder Regularity for Variable Coefficients ........... 395
15.6.Hölder-Caccioppoli Estimates .......................... 398
15.7.Quasilinear Equations ................................. 400
16.Applications to Partial Differential Equations ............. 403
16.1.The Hodge * Method .................................... 404
16.1.1.Equations of Divergence Type: The A-Harmonic
Operator ....................................... 405
16.1.2.The Natural Domain of Definition ............... 406
16.1.3.The Л-Harmonic Conjugate Function .............. 408
16.1.4.Regularity of Solutions ........................ 409
16.1.5.General Linear Divergence Equations ............ 411
16.1.6.А-Harmonic Fields .............................. 414
16.2.Topological Properties of Solutions ................... 418
16.3.The Hodographic Method ................................ 420
16.3.1.The Continuity Equation ........................ 420
16.3.2.The p-Harmonic Operator div|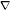 |Р-2 |Р-2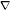 ............. 423
16.3.3.Second-Order Derivatives ....................... 424
16.3.4.The Complex Gradient ........................... 427
16.3.5.Hodograph Transform for the p-Laplacian ........ 430
16.3.6.Sharp Holder Regularity for p-Harmonic
Functions ...................................... 431
16.3.7.Removing the Rough Regularity in the
Gradient ....................................... 432
16.4.The Nonlinear ............. 423
16.3.3.Second-Order Derivatives ....................... 424
16.3.4.The Complex Gradient ........................... 427
16.3.5.Hodograph Transform for the p-Laplacian ........ 430
16.3.6.Sharp Holder Regularity for p-Harmonic
Functions ...................................... 431
16.3.7.Removing the Rough Regularity in the
Gradient ....................................... 432
16.4.The Nonlinear 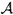 -Harmonic Equation .................... 433
16.4.1.δ-Monotonicity of the Structural Field ......... 435
16.4.2.The Dirichlet Problem .......................... 441
16.4.3.Quasiregular Gradient Fields and
С1,α-Regularity ................................ 445
16.5.Boundary Value Problems ............................... 449
16.5.1.A Nonlinear Riemann-Hilbert Problem ............ 452
16.6.G-Compactness of Beltrami Differential Operators ...... 456
16.6.1.G-Convergence of the Operators -Harmonic Equation .................... 433
16.4.1.δ-Monotonicity of the Structural Field ......... 435
16.4.2.The Dirichlet Problem .......................... 441
16.4.3.Quasiregular Gradient Fields and
С1,α-Regularity ................................ 445
16.5.Boundary Value Problems ............................... 449
16.5.1.A Nonlinear Riemann-Hilbert Problem ............ 452
16.6.G-Compactness of Beltrami Differential Operators ...... 456
16.6.1.G-Convergence of the Operators 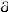 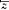 - μj - μj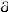 z ........ 457
16.6.2.G-Limits and the Weak*-Topology ................ 459
16.6.3.The Jump from z ........ 457
16.6.2.G-Limits and the Weak*-Topology ................ 459
16.6.3.The Jump from 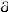 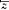 — υ — υ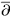 z to z to 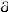 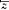 - μ - μ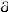 z ............. 461
16.6.4.The Adjacent Operator's Two Primary
Solutions ...................................... 462
16.6.5.The Independence of Фz(z) and ψz{z) ............. 463
16.6.6.Linear Families of Quasiregular Mappings ....... 464
16.6.7.G-Compactness for Beltrami Operators ........... 467
17.PDEs Not of Divergence Type: Pucci's Conjecture ............ 472
17.1.Reduction to a First-Order System ..................... 475
17.2.Second-Order Caccioppoli Estimates .................... 476
17.3.The Maximum Principle and Pucci's Conjecture .......... 478
17.4.Interior Regularity ................................... 481
17.5.Equations with Lower-Order Terms ...................... 483
17.5.1.The Dirichlet Problem .......................... 486
17.6.Pucci's Example ....................................... 488
18.Quasiconformal Methods in Impedance Tomography:
Calderon's Problem ......................................... 490
18.1.Complex Geometric Optics Solutions .................... 493
18.2.The Hilbert Transform z ............. 461
16.6.4.The Adjacent Operator's Two Primary
Solutions ...................................... 462
16.6.5.The Independence of Фz(z) and ψz{z) ............. 463
16.6.6.Linear Families of Quasiregular Mappings ....... 464
16.6.7.G-Compactness for Beltrami Operators ........... 467
17.PDEs Not of Divergence Type: Pucci's Conjecture ............ 472
17.1.Reduction to a First-Order System ..................... 475
17.2.Second-Order Caccioppoli Estimates .................... 476
17.3.The Maximum Principle and Pucci's Conjecture .......... 478
17.4.Interior Regularity ................................... 481
17.5.Equations with Lower-Order Terms ...................... 483
17.5.1.The Dirichlet Problem .......................... 486
17.6.Pucci's Example ....................................... 488
18.Quasiconformal Methods in Impedance Tomography:
Calderon's Problem ......................................... 490
18.1.Complex Geometric Optics Solutions .................... 493
18.2.The Hilbert Transform 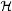 σ .............................. 495
18.3.Dependence on Parameters .............................. 497
18.4.Nonlinear Fourier Transform ........................... 499
18.5.Argument Principle .................................... 502
18.6.Subexponential Growth ................................. 504
18.7.The Solution to Calderon's Problem .................... 510
19.Integral Estimates for the Jacobian ........................ 514
19.1.The Fundamental Inequality for the Jacobian ........... 514
19.2.Rank-One Convexity and Quasiconvexity ................. 518
19.2.1.Burkholder's Theorem ........................... 521
19.3.L^Integrability of the Jacobian ....................... 523
20.Solving the Beltrami Equation: Degenerate Elliptic Case .... 527
20.1.Mappings of Finite Distortion; Continuity ............. 529
20.1.1.Topological Monotonicity ....................... 530
20.1.2.Proof of Continuity in W1,2 .................... 534
20.2.Integrable Distortion; W1,2-Solutions and Their
Properties ............................................ 534
20.3.A Critical Example .................................... 540
20.4.Distortion in the Exponential Class ................... 543
20.4.1.Example: Regularity in Exponential
Distortion ..................................... 543
20.4.2.Beltrami Operators for Degenerate Equations .... 545
20.4.3.Decay of the Neumann Series .................... 549
20.4.4.Existence Above the Critical Exponent .......... 554
20.4.5.Exponential Distortion: Existence of
Solutions ...................................... 557
20.4.6.Optimal Regularity ............................. 560
20.4.7.Uniqueness of Principal Solutions .............. 563
20.4.8.Stoilow Factorization .......................... 564
20.4.9.Failure of Factorization in W1,q When q < 2 ..... 567
20.5.Optimal Orlicz Conditions for the Distortion
Function .............................................. 570
20.6.Global Solutions ...................................... 576
20.6.1.Solutions on σ .............................. 495
18.3.Dependence on Parameters .............................. 497
18.4.Nonlinear Fourier Transform ........................... 499
18.5.Argument Principle .................................... 502
18.6.Subexponential Growth ................................. 504
18.7.The Solution to Calderon's Problem .................... 510
19.Integral Estimates for the Jacobian ........................ 514
19.1.The Fundamental Inequality for the Jacobian ........... 514
19.2.Rank-One Convexity and Quasiconvexity ................. 518
19.2.1.Burkholder's Theorem ........................... 521
19.3.L^Integrability of the Jacobian ....................... 523
20.Solving the Beltrami Equation: Degenerate Elliptic Case .... 527
20.1.Mappings of Finite Distortion; Continuity ............. 529
20.1.1.Topological Monotonicity ....................... 530
20.1.2.Proof of Continuity in W1,2 .................... 534
20.2.Integrable Distortion; W1,2-Solutions and Their
Properties ............................................ 534
20.3.A Critical Example .................................... 540
20.4.Distortion in the Exponential Class ................... 543
20.4.1.Example: Regularity in Exponential
Distortion ..................................... 543
20.4.2.Beltrami Operators for Degenerate Equations .... 545
20.4.3.Decay of the Neumann Series .................... 549
20.4.4.Existence Above the Critical Exponent .......... 554
20.4.5.Exponential Distortion: Existence of
Solutions ...................................... 557
20.4.6.Optimal Regularity ............................. 560
20.4.7.Uniqueness of Principal Solutions .............. 563
20.4.8.Stoilow Factorization .......................... 564
20.4.9.Failure of Factorization in W1,q When q < 2 ..... 567
20.5.Optimal Orlicz Conditions for the Distortion
Function .............................................. 570
20.6.Global Solutions ...................................... 576
20.6.1.Solutions on 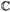 ................................. 576
20.6.2.Solutions on ................................. 576
20.6.2.Solutions on 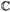 ................................. 578
20.7.A Liouville Theorem ................................... 579
20.8.Applications to Degenerate PDEs ....................... 580
20.9.Lehto's Condition ..................................... 581
21.Aspects of the Calculus of Variations ...................... 586
21.1.Minimizing Mean Distortion ............................ 586
21.1.1.Formulation of the General Problem ............. 588
21.1.2.The L1-Grötzsch Problem ........................ 588
21.1.3.Sublinear Growth: Failure of Minimization ...... 591
21.1.4.Inverses of Homeomorphisms of Integrable
Distortion ..................................... 592
21.1.5.The Traces of Mappings with Integrable
Distortion ..................................... 595
21.2.Variational Equations ................................. 599
21.2.1.The Lagrange-Euler Equations ................... 601
21.2.2.Equations for the Inverse Map .................. 604
21.3.Mean Distortion, Annuli and the Nitsche Conjecture .... 606
21.3.1.Polar Coordinates .............................. 611
21.3.2.Free Lagrangiaus ............................... 612
21.3.3.Lower Bounds by Free Lagrangians ............... 613
21.3.4.Weighted Mean Distortion ....................... 615
21.3.5.Minimizers within the Nitsche Range ............ 616
21.3.6.Beyond the Nitsche Bound ....................... 618
21.3.7.The Minimizing Sequence and Its BV-limit ....... 619
21.3.8.Correction Lemma ............................... 622
Appendix: Elements of Sobolev Theory and Function Spaces ...... 624
A.l. Schwartz Distributions ........................... 624
A.2. Definitions of Sobolev Spaces .................... 627
A.3. Mollification .................................... 628
A.4. Pointwise Coincidence of Sobolev Functions ....... 630
A.5. Alternate Characterizations ...................... 630
A.6. Embedding Theorems ............................... 633
A.7. Duals and Compact Embeddings ..................... 636
A.8. Hardy Spaces and BMO ............................. 637
A.9. Reverse Hölder Inequalities ...................... 640
A.10.Variations of Sobolev Mappings ................... 640
Basic Notation ................................................ 643
Bibliography .................................................. 647
Index ......................................................... 671 ................................. 578
20.7.A Liouville Theorem ................................... 579
20.8.Applications to Degenerate PDEs ....................... 580
20.9.Lehto's Condition ..................................... 581
21.Aspects of the Calculus of Variations ...................... 586
21.1.Minimizing Mean Distortion ............................ 586
21.1.1.Formulation of the General Problem ............. 588
21.1.2.The L1-Grötzsch Problem ........................ 588
21.1.3.Sublinear Growth: Failure of Minimization ...... 591
21.1.4.Inverses of Homeomorphisms of Integrable
Distortion ..................................... 592
21.1.5.The Traces of Mappings with Integrable
Distortion ..................................... 595
21.2.Variational Equations ................................. 599
21.2.1.The Lagrange-Euler Equations ................... 601
21.2.2.Equations for the Inverse Map .................. 604
21.3.Mean Distortion, Annuli and the Nitsche Conjecture .... 606
21.3.1.Polar Coordinates .............................. 611
21.3.2.Free Lagrangiaus ............................... 612
21.3.3.Lower Bounds by Free Lagrangians ............... 613
21.3.4.Weighted Mean Distortion ....................... 615
21.3.5.Minimizers within the Nitsche Range ............ 616
21.3.6.Beyond the Nitsche Bound ....................... 618
21.3.7.The Minimizing Sequence and Its BV-limit ....... 619
21.3.8.Correction Lemma ............................... 622
Appendix: Elements of Sobolev Theory and Function Spaces ...... 624
A.l. Schwartz Distributions ........................... 624
A.2. Definitions of Sobolev Spaces .................... 627
A.3. Mollification .................................... 628
A.4. Pointwise Coincidence of Sobolev Functions ....... 630
A.5. Alternate Characterizations ...................... 630
A.6. Embedding Theorems ............................... 633
A.7. Duals and Compact Embeddings ..................... 636
A.8. Hardy Spaces and BMO ............................. 637
A.9. Reverse Hölder Inequalities ...................... 640
A.10.Variations of Sobolev Mappings ................... 640
Basic Notation ................................................ 643
Bibliography .................................................. 647
Index ......................................................... 671
|